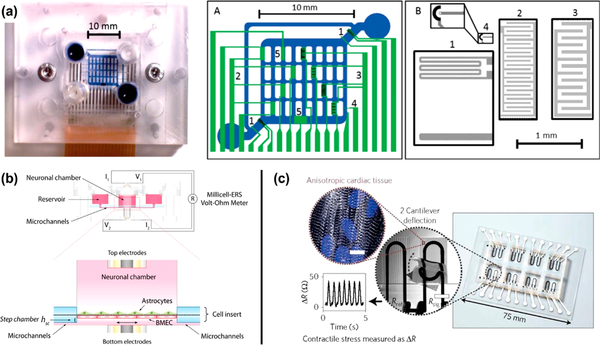
Figure 2.
Microphysiological systems with developmental sensors. (a) On-chip electrothermal micropumps (1), interdigitated electrodes (2, 3), oxygen sensors (4), and pH sensors (5) are all integrated into a single MPS to observe cell proliferation and viability. Reprinted with permission from Bonk 2015.94 Copyright 2015 MDPI AG. (b) A blood–brain barrier MPS includes neural and endothelial cell growth chambers with applied shear as well as embedded electrodes connected to a volt–ohm meter to measure transendothelial electrical resistance as a metric of BBB development. Reprinted with permission from Wang 2017.58 Copyright 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. (c) 3D printed strain sensors are integrated into an MPS, using cantilever deflection to determine cardiomyocyte self-assembly in engineered tissue. Reprinted with permission from Lind 2017.38 Copyright 2017 Macmillan Publishers Limited.