Figure 1.
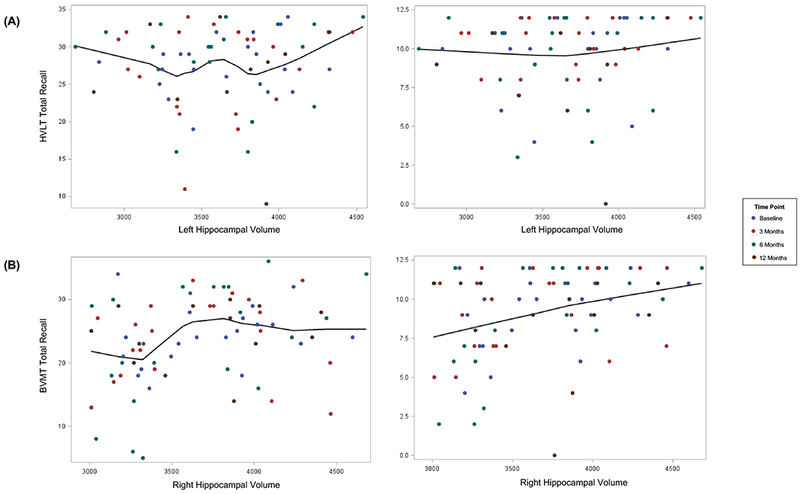
(A) Smaller left hippocampal volumes were not significantly associated with poorer performance on verbal memory testing (HVLT-R Total Recall β2= 0.00038, P=.849; HVLT-R Delayed Recall, β2= 0.00008, P=.935).
(B) Smaller right hippocampal volumes were significantly associated with worse performance on visuospatial memory testing (BVMT-R Total Recall, β2= 0.004 points/mm3, P=.069; BVMT-R Delayed Recall, β2= 0.00214 points/mm3, P=.021). Abbreviations: BVMT-R, Brief Visuospatial Memory Test-Revised; HVLT-R, Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised
