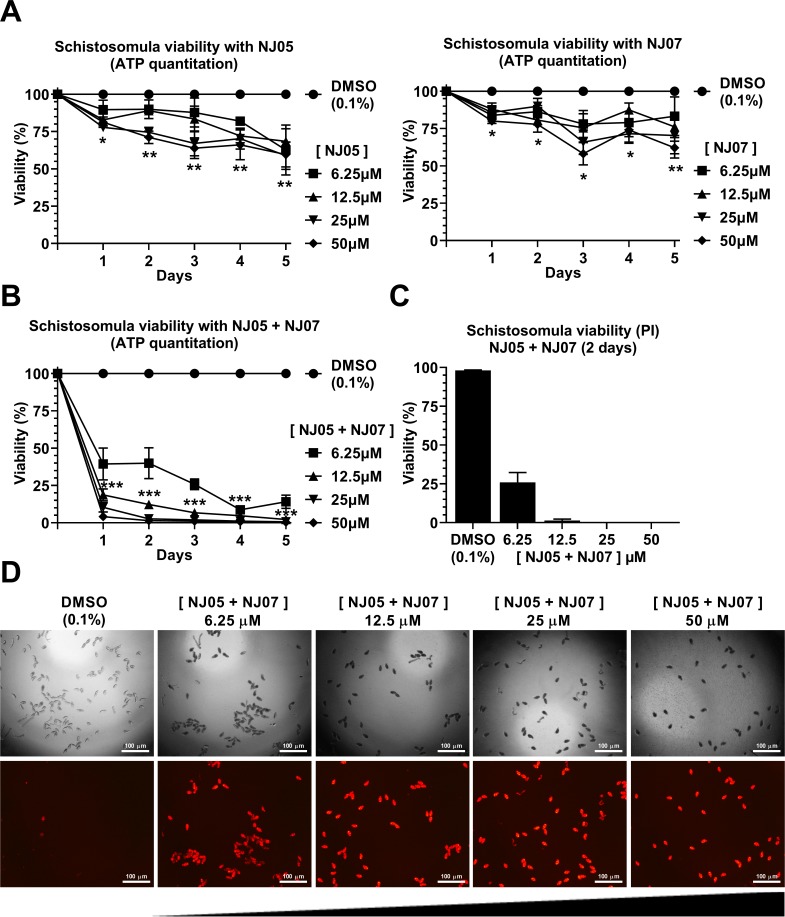
Fig 2. Effect of NJ05, NJ07 or NJ05 + NJ07 on schistosomula viability.
(A and B) ATP quantitation using a luminescent assay to assess schistosomula viability under NJ series compounds exposure. Schistosomula (100-120/well) were incubated with the indicated concentrations of NJ05, NJ07, NJ05 + NJ07 or with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for up to 5 days. Viability was expressed as % luminescence values relative to the control (DMSO). Mean ± SEM from three biological replicate experiments are shown. The two-way ANOVA test was used to calculate the statistical significance (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). For clarity purposes, we show only the highest p-value obtained from the two-way ANOVA test for each time point on all different concentrations tested. (C) Quantitation of schistosomula viability using propidium iodide staining; schistosomula were treated for two days with NJ05 + NJ07 at the different concentrations indicated. Percentage of viable schistosomula (non-stained with propidium iodide) is shown. For each condition tested, about 400 schistosomula were used, divided into four biological replicates. Mean ± SEM from four replicate experiments are shown. (D) Schistosomula treated with the indicated concentrations of NJ05 + NJ07 or with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for 2 days were visualized by staining with propidium iodide (marker of dead cells; 572 nm emission filter microscope). For each concentration (indicated at the top), the upper panel shows a light microscopy image and the bottom panel shows the image of the same field with differential fluorescence detection of PI-positive parasites. Bar = 100 μm.