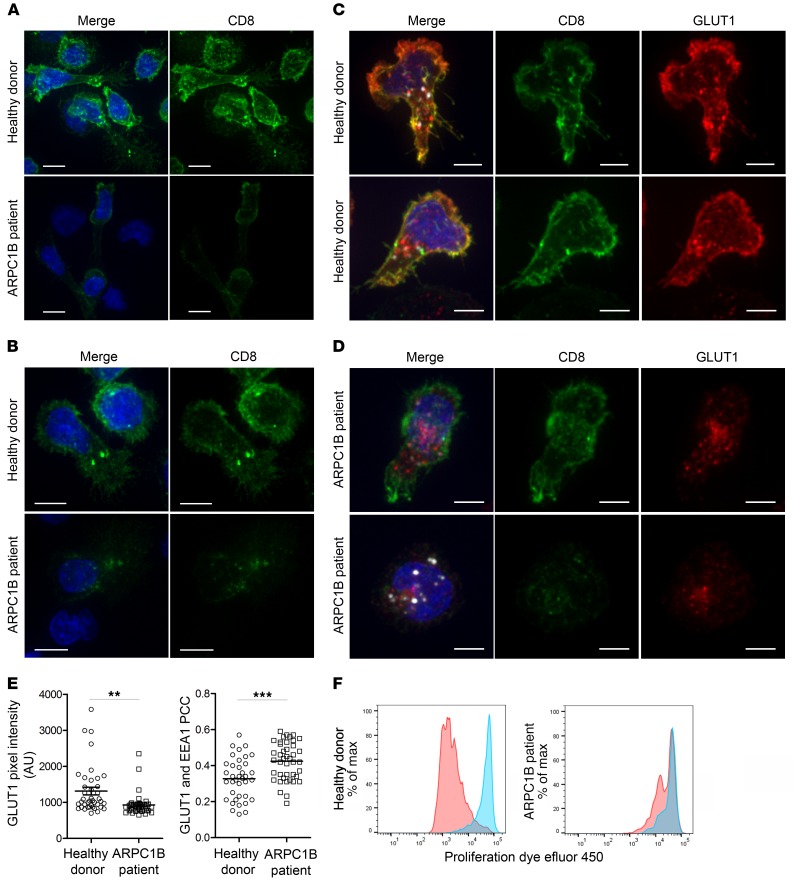
Figure 7. Absence of ARPC1B alters surface expression of CD8 and GLUT1 in hCTLs.
(A–D) HD and ARPC1B-deficient patient hCTLs were fixed in PFA for 20 minutes, permeabilized, and stained with an antibody against CD8 alone (green) (A and B) or in combination with anti-GLUT1 (red) and anti-EEA1 (white) antibodies (C and D). Images are 3D reconstructions of Z-stack. Scale bars: 4 μm. (E) Measurement of the mean intensity of GLUT1 expressed in AU and the degree of colocalization with EEA1 expressed as PCC (see Methods) in HD and ARPC1B-deficient patient hCTLs based on images as sampled in C and D. HD, n = 41 cells; ARPC1B-deficient patient, n = 38 cells. P < 0.005 (unpaired t test). **P < 0.0013; ***P < 0.0002. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of the proliferation capacity of HD and ARPC1B-deficient patient hCTLs (gated on live CD8+ cells) in the absence (blue) or presence (red) of plate-bound anti-CD3 stimulation (1 μg/mL). All data are representative of 3 independent experiments.