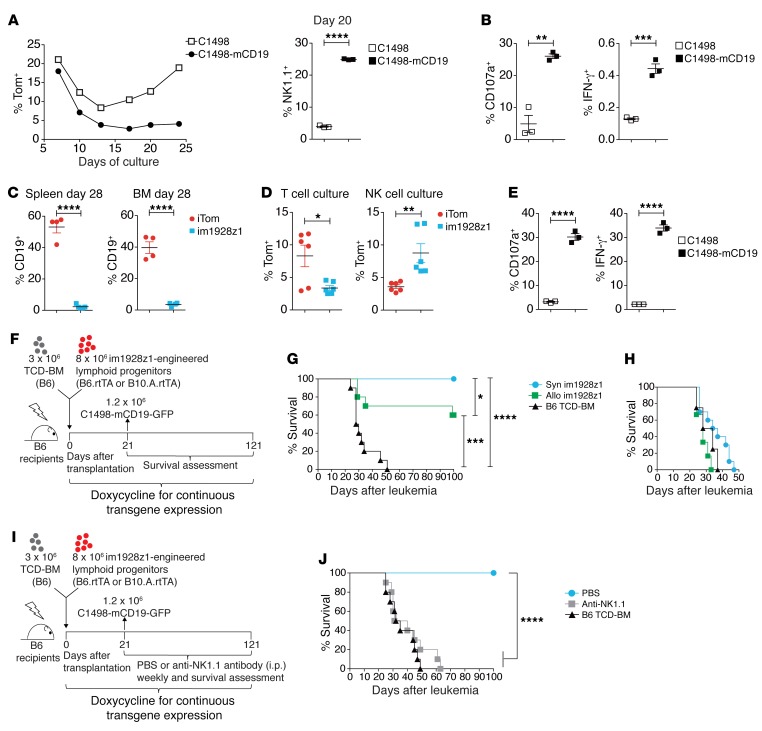
Figure 2. CARiK cells derived from im1928z1-engineered lymphoid progenitors demonstrate potent antileukemic activity across MHC barriers in vivo.
(A) Generation of either stimulated or nonstimulated im1928z1‑generated lymphoid progenitors. Frequencies of Tom+ progenitors (left) and NK1.1+ im1928z1-CARiK cells on day 20 of culture (right). (B) Responses of im1928z1-generated lymphoid progenitors upon stimulation were quantified via CD107a degranulation (left) or IFN-γ production (right). Data from 1 of 2 experiments are shown. (C) CD19+ B cell recovery of irradiated B6 recipients of B6 TCD-BM and either im1928z1-engineered progenitors or iTom controls (n = 4 mice, respectively). (D) Splenocytes were harvested on day 28 and recultured ex vivo under T cell or NK cell culture conditions (n = 6; left). (E) CD107a+ degranulation (middle) and IFN-γ (right) responses to antigen were assessed (n = 3). (A–E) Student’s t test was used for analysis. Data represent mean ± SEM. (F and G) B6 recipients of 3 × 106 B6 TCD-BM (n = 10/group) with or without 8 × 106 syngeneic (syn) or MHC class I and II mismatched (allo) im1928z1-expressing progenitors received 1.2 × 106 C1498-mCD19 cells on day 21 after transplantation and were monitored for survival. Results from 1 of 2 independent experiments are graphed. (H) Survivors were rechallenged with 1.2 × 106 C1498-mCD19 cells on day 100 and reassessed for survival. TCD-BM–only recipients (n = 4) were added for control. (I and J) B6 recipients of 3 × 106 B6 TCD-BM with or without 8 × 106 syngeneic im1928z1-engineered lymphoid progenitors were treated with weekly i.p. injections of an anti-NK1.1 antibody (clone: PK136; 200 μg/dose). PBS was used for control (n = 10 per group). All mice were challenged with 1.2 × 106 C1498-mCD19 cells on day 21 after transplantation (J). Survival curves were compared using Mantel-Cox (log-rank) test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.