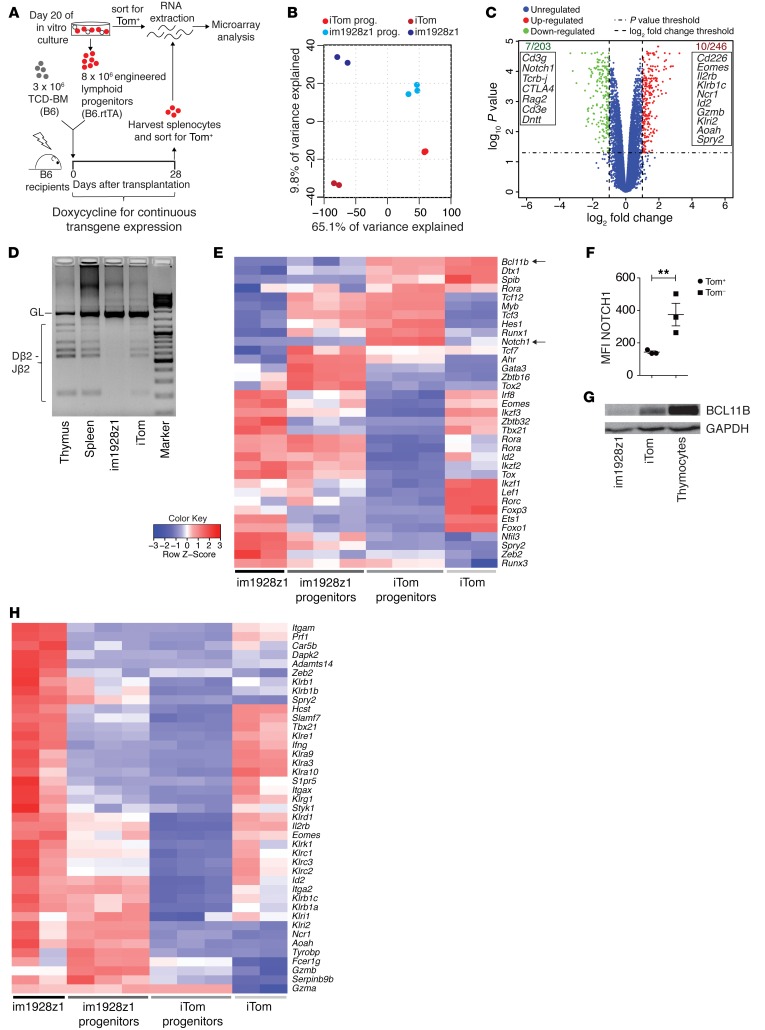
Figure 3. im1928z1 expression on HSPCs leads to BCL11B suppression, allowing for CARiK cell development, and concomitantly decreases T cell–associated gene expression.
(A) For microarray data analysis, RNA from Tom+-sorted im1928z1-generated lymphoid progenitors (n = 3) or iTom‑engineered lymphoid progenitors (n = 3) immediately previous to cotransplantation or from spleen-derived progeny (n = 2, respectively) were isolated on day 28 after transplantation. (B) PCA of total transcriptome profiles from either engineered lymphoid progenitors or their respective progeny is graphed. (C) Volcano plot for comparison of differently regulated transcripts in im1928z1-generated lymphoid progenitors and iTom controls. Gene symbols in the boxes indicate selected transcripts found to be downregulated (green) or upregulated (red) at least 2-fold (P < 0.05) in im1928z1-generated lymphoid progenitors as compared with controls. (D) Recombination of D and J regions of the TCRβ locus in engineered lymphoid progenitors. Genomic DNA of engineered progenitors was isolated on day 20 of culture, and rearrangements were detected by PCR. Splenocytes and thymocytes from WT B6 mice were used as controls. Results from 1 of 2 independent experiments are shown. GL, germ line band. (E) Heatmap showing the relative expression of transcripts for selected TFs. Data are normalized according to expression in each row. (F) NOTCH1 expression on transgene-positive (Tom+) or transgene-negative (Tom–) lymphoid progenitors engineered with im1928z1. Student’s t test was used. Data represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01. (G) Western blot analysis for BCL11B in lysates from iTom lymphoid progenitors, im1928z1-generated lymphoid progenitors, or B6 WT thymocytes. Representative data from 1 of 2 independent experiments are shown. (H) Relative expression of selected transcripts for NK cell receptors, integrins, adaptors, effector molecules, and TFs in engineered lymphoid progenitors and their progeny. Data are normalized according to expression in each row.