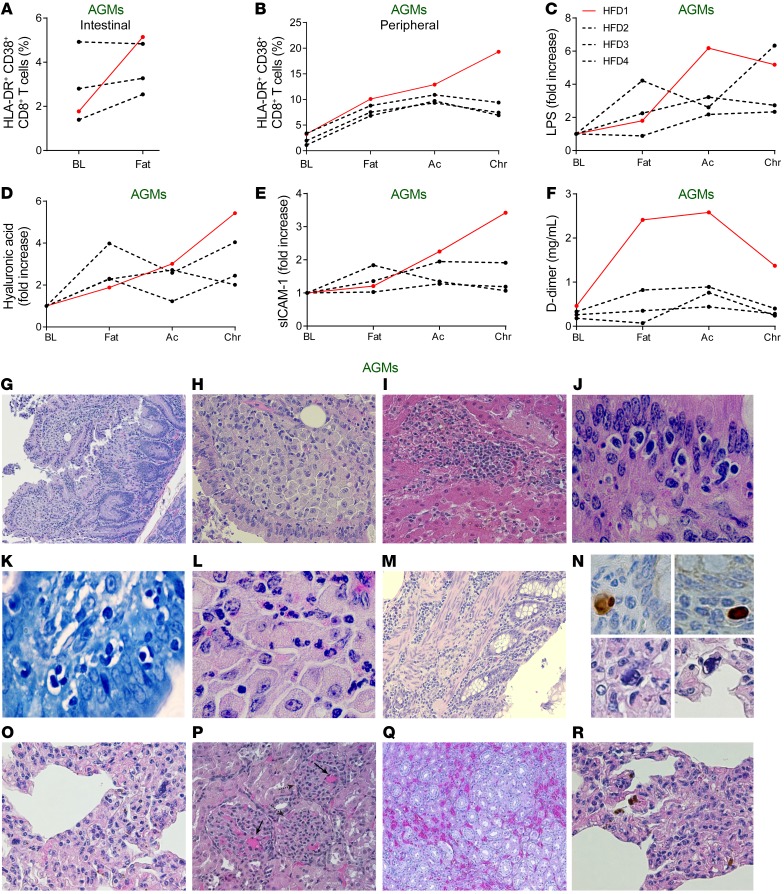
Figure 3. Elevated biomarkers and pathologic changes of the HFD-receiving AGMs that progressed to AIDS-like disease.
HFD-receiving AGM HFD1 developed an AIDS-like disease, with distinctly elevated levels of HLA-DR and CD38 coexpressing CD8+ T cells in the intestine (A) and periphery (B), LPS (C), hyaluronic acid (D), sICAM-1 (E), and D-dimer (F), as compared with the remaining 3 AGMs on HFD. Ac, acute infection; BL, baseline (preinfection pre-HFD); Chr, chronic infection; Fat, preinfection post-HFD. Representative H&E images of lesions for AIDS and SIV-associated comorbidities from HFD1. (G) Enteritis, with disrupted intestinal architecture, irregular crypts, enlarged villi, and alteration of the surface epithelium. (H) Numerous foamy macrophages in the lamina propria of the small intestine suggestive for active atypical mycobacterial disease. (I) Hepatic granulomas, suggestive of atypical mycobacterial disease. (J) Cystoisospora belli present in vacuoles in the intestinal epithelium. (K) Giemsa-staining confirmation of small intestine C. belli infection. (L) Eosinophil infiltration in the small intestine, characteristic for parasitic infections. (M) Colitis, with disrupted intestinal architecture, atrophic crypts and mononuclear cell infiltration of the mucosa, submucosa, and of the muscle layers. (N) Upper panels: CMV immunohistochemistry, with positive cells in the colon. Lower panels: Numerous large cells in the lung, with nuclear and cytoplasmic viral inclusions characteristic for CMV infection (detail of O). (O) Interstitial pneumonia, with thickened alveolar walls due to infiltration with mononuclear cells. (P) Numerous microthrombi in the kidney glomeruli indicative of TMA (solid arrow). Disrupted kidney cortex architecture with irregular, small fibrotic glomeruli, pathognomonic for chronic glomerulonephritis (dashed arrow). (Q) Enlarged capillaries in the kidney parenchyma indicative of chronic stasis associated with heart failure. (R) Numerous hemosiderin-laden macrophages in the lung, indicative of chronic stasis associated with heart failure. Original magnifications: ×200 (G–I, M, and O–R); ×400 (L); ×600 (J, K, and N).