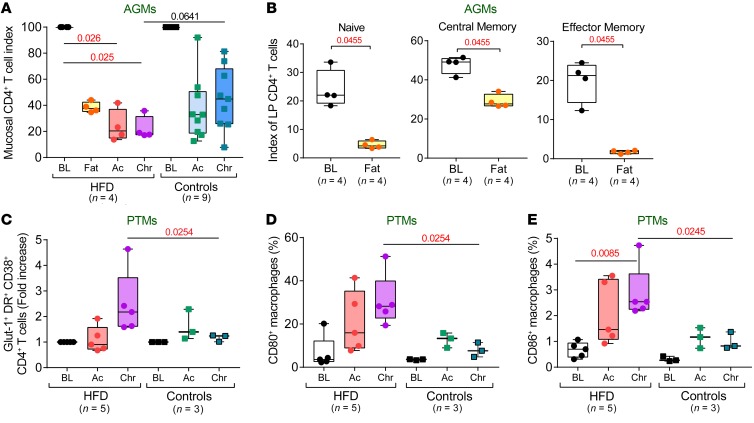
Figure 6. HFD alters gut immune environment and activation states of the immune cells.
(A) Mucosal CD4+ T cell depletion in HFD-receiving and control AGMs is shown as an index of baseline levels and compared at key time points of SIV infection within the HFD group with Friedman test corrected for multiple comparisons, and between HFD and control groups with Kruskal-Wallis test. (B) Mucosal-naïve, central memory, and effector memory CD4+ T cells are shown as an index of total baseline mucosal CD4+ T cell levels and compared before and after HFD in preinfection AGMs with Friedman test. Frequencies of Glut-1, HLA-DR, and CD38 coexpressing CD4+ T cells (C), as well as CD80-expressing (D) and CD86-expressing (E) macrophages in the intestine of PTMs are compared at key time points of SIV infection within HFD group with Friedman test corrected for multiple comparisons and between HFD and control groups with Kruskal-Wallis test. Data are presented as individual values with medians. Sample size (n) and P values are presented on graphs. Ac, acute infection; BL, baseline (preinfection pre-HFD); Chr, chronic infection; Fat, preinfection post-HFD.