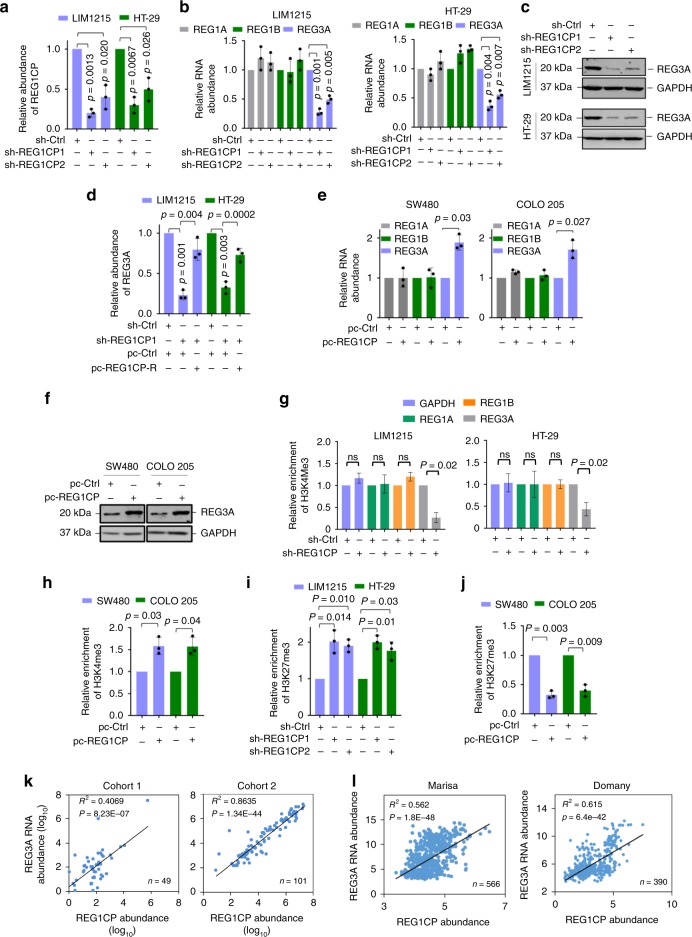
Fig. 2.
REG1CP promotes transcription of REG3A. a–c Silencing of REG1CP (a) decreased REG3A mRNA (b) and protein levels (c). d Co-introduction of a shRNA-resistant REG1CP mutant (REG1CP-R) diminished the inhibitory effect of REG1CP silencing on REG3A mRNA expression. e, f Overexpression of REG1CP increased REG3A mRNA (e) and protein (f) levels. g, h Silencing of REG1CP decreased (g) whereas overexpression of REG1CP (h) increased enrichment of H3K4me3 to REG3A promoter, but not to REG1A or REG1B promoter (g). Relative enrichment of H3K4me3 to the -7/-109 fragment of REG3A promoter was measured using ChIP-qPCR assays in LIM1215 and HT-29 cells after silencing (g) or in SW480 and COLO205 cells after overexpression (h) of REG1CP. i, j Silencing of REG1CP increased (i) whereas overexpression of REG1CP decreased (j) enrichment of H3K27me3 to REG3A proximal promoter. Relative enrichment of H3K27me3 at the -7/-109 fragment of REG3A promoter was measured using ChIP-qPCR assays in LIM1215 and HT-29 cells after silencing (i) or in SW480 and COLO205 cells after overexpression (j) of REG1CP. k, l Regression analysis of the relationship between REG3A mRNA and REG1CP expression in two cohorts of colon cancer samples determined using qPCR (k) and in published datasets acquired from the R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform (l). n = 3 independent experiments unless specified differently. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM (a, b, d, e, g–j) or representatives (c, f). Statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed t-test unless specified.