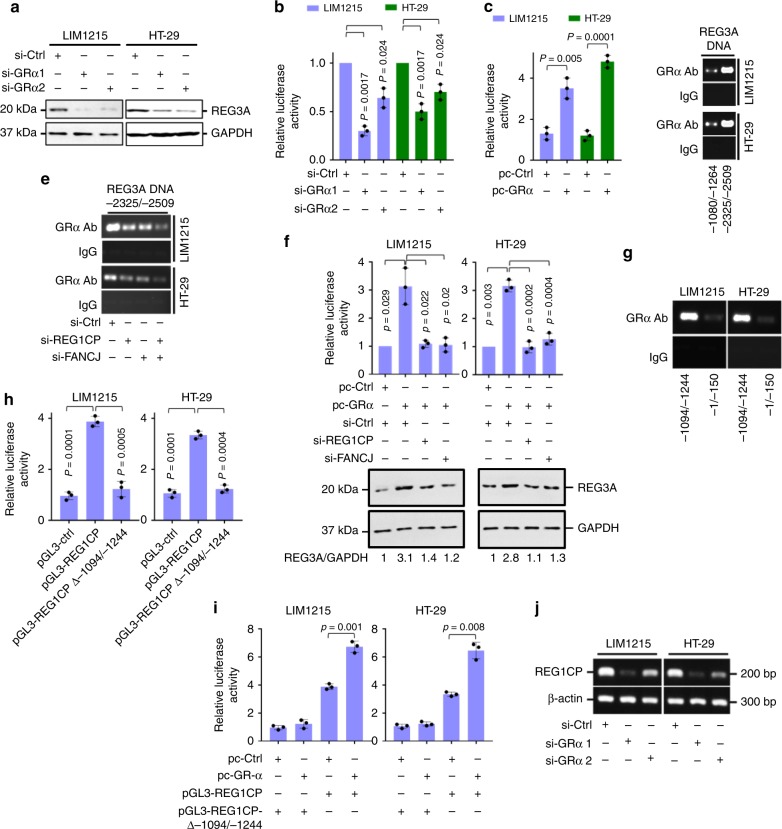
Fig. 7.
GRα is responsible for transcriptional activation of REG3A and REG1CP. a GRα silencing reduced REG3A expression. b, c GRα silencing reduced (b) whereas its overexpression increased (c) luciferase reporter activity of pGL3-basic based REG3 promoter constructs. d GRα bound to the 2325/-2509 fragment of REG3A promoter. The precipitates of an antibody against GRα from formaldehyde-cross-linked chromatin of cells were subjected to qPCR using primers directed to indicated fragments of REG3A promoter. e Silencing of REG1CP or FANCJ reduced the association between GRα and the 2325/-2509 fragment of REG3A promoter as shown using ChIP assays. f Silencing of REG1CP or FANCJ diminished the increase in luciferase reporter activity of pGL3-basic based REG3 promoter constructs (upper) and the upregulation of endogenous REG3A protein levels (lower) caused by overexpression of GRα. The number below each western blot lane represents the level of REG3A protein relative the level of GAPDH expression. g GRα bound to the −1094/−1244 fragment of REG1CP promoter as measured using ChIP assays. h Deletion of the −1094/−1244 fragment abolished luciferase reporter activity of pGL3-basic based REG1CP promoter constructs. i Overexpression of GRα increased luciferase reporter activity of pGL3-basic based REG1CP promoter constructs with the −1094/−1244 fragment. j GRα silencing decreased endogenous REG1CP expression. n = 3 independent experiments. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM (b, c, f (upper), h, i) or representatives (a, d, e, f (lower), g, j). Statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed t-test.