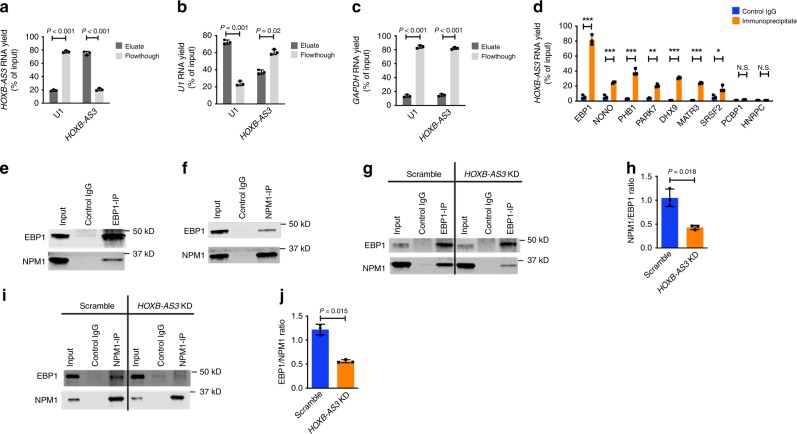
Fig. 4.
EBP1 strongly interacts with HOXB-AS3 in NPM1mut AML cells. a–c Yields of a HOXB-AS3 RNA, b U1 RNA, and c GAPDH RNA in the eluates and the flow-through of lysates hybridized with U1 and HOXB-AS3-targeting probes. The RNA yield is depicted as a percentage of the amount of the respective transcript in the input sample. d Validation of HOXB-AS3-protein interactions via RNA-Immunoprecipitation (RIP) experiments with nine candidate proteins. Enrichment of each immunoprecipitate is compared with the respective IgG control (mouse or rabbit). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001, N.S., not significant. e Immunoprecipitation of the EBP1 protein in nuclear lysates of OCI-AML3 cells followed by western blotting (WB) for the EBP1 and NPM1 proteins. f Immunoprecipitation of the NPM1 protein in nuclear lysates of OCI-AML3 cells followed by WB for the EBP1 and NPM1 proteins. g–j Effect of HOXB-AS3 depletion (HOXB-AS3 KD) on the formation of the EBP1-NPM1 complex in OCI-AML3 cells: g EBP1 immunoprecipitation in scramble versus HOXB-AS3 KD-treated cells followed by WB for the EBP1 and NPM1 proteins. h Quantification of three independent experiments. i NPM1 immunoprecipitation in scramble versus HOXB-AS3 KD-treated cells followed by WB for the EBP1 and NPM1 proteins. j Quantification of three independent experiments. P values were calculated using paired two-sided t-tests. In the figures, heights of boxplots indicate mean values with standard deviation. Error bars indicate highest and lowest values in each population. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.