Figure 5.
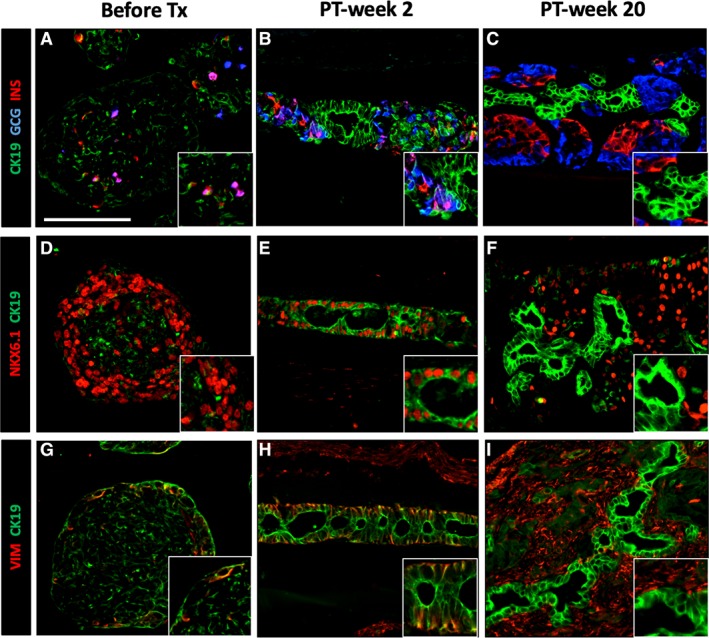
Transient CK19‐expression in pancreatic progenitor cells in human induced pluripotent stem cell‐derived pancreatic endoderm (hiPS‐PE) implants. In situ histological analysis of device‐encapsulated hiPS‐PE implants at post‐transplant (PT)‐week 2 and 20, comparison with start preparation. The preparation at start contained 45%–55% PDX1+/NKX6.1+/hormone‐negative cells that are considered as pancreatic progenitors; they exhibited a weak and spotty CK19‐positivity (A, D, G). At PT‐week 2 (B, E, H), the majority of PDX1+/NKX6.1+ cells stained strongly positive for cytokeratin‐19 (CK19) with vimentin‐positivity (VIM) at their basal pole; they formed an epithelial cell layer around small cysts Adjacent cell clusters contained weakly CK19+ cells associated to small numbers of hormone‐positive cells (insulin, glucagon). At PT‐week 20 (C, F, I), the epithelial cell layer was formed by CK19‐positive that were negative for PDX1, NKX6.1, and VIM, while adjacent cell clusters contained PDX1+/NKX6.1+/insulin‐positive cells. Scale bar: 100 μm.
