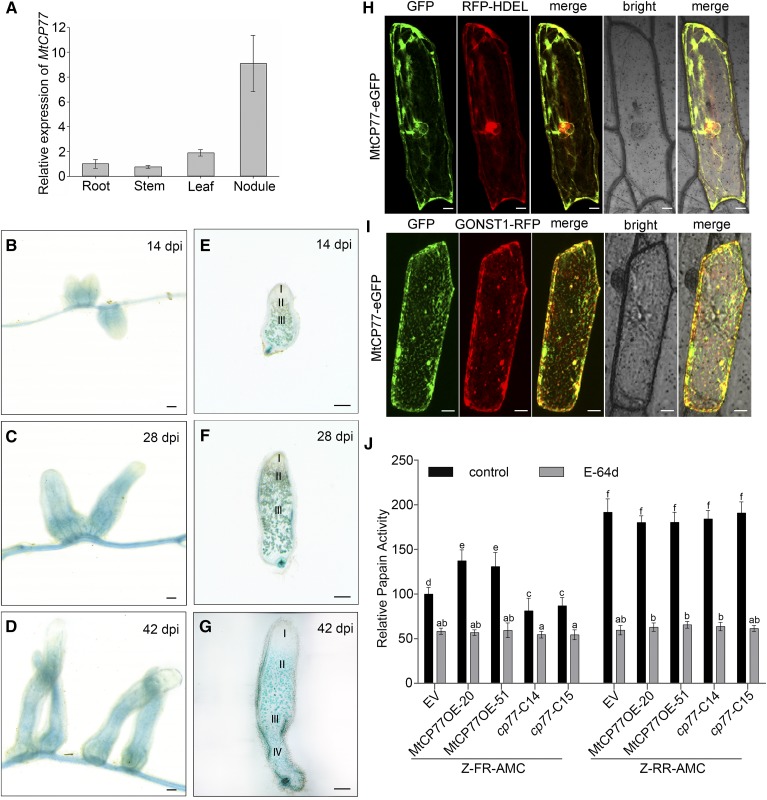
Figure 7.
Expression pattern and Cys protease activity of MtCP77. A, The relative expression of MtCP77 in the roots, stems, leaves, and nodules of wild-type plants at 28 dpi with S. meliloti 1021 was quantified by RT-qPCR using MtACTIN as the reference gene. The error bars represent the ± sd of the means of two biological replicates. B to G, GUS staining of MtCP77 expressed in M. truncatula nodules. The expression pattern of the 2-kb promoter region of MtCP77 was detected. B to D, GUS staining of nodules on stable transgenic plants at 14 (B), 28 (C), and 42 dpi (D). E to G, Sections of nodules at 14 (E), 28 (F), and 42 dpi (G). The section thickness is 80 μm. The different zones of the nodules (I–IV) are shown. I, Meristematic zone; II, infection zone; III, nitrogen fixation zone; IV, senescence zone. Bars = 1 mm. H and I, Subcellular localization of MtCP77 in onion epidermal cells. MtCP77-eGFP fusion protein driven by the CaMV35S promoter was transiently coexpressed with RFP-HDEL (ER marker, H) and GONST1-RFP (Golgi marker, I) in onion epidermal cells via particle bombardment. The fluorescence signals, i.e. GFP and RFP, were detected by CLSM using excitation wavelengths of 488 nm and 546 nm, respectively. Bars = 20 μm. J, The Cys protease activity of MtCP77 in EV, MtCP77OE, and Mtcp77. The protein extracts of roots of EV, MtCP77OE, and Mtcp77 at 14 dpi were used to characterize their proteinase activity. The Cys activity of MtCP77 was assayed for Z-FR-AMC (cathepsin-l) and Z-RR-AMC (cathepsin-B) proteolytic activity, and the papain inhibitor E-64d was used to inhibit the Cys protease activity. The data are represented as a percentage of the Z-FR-AMC proteolytic activity of the EV. The error bars represent the means ± sd of three biological replicates, and significant differences were determined with ANOVA with a post-hoc Tukey test and are indicated by letters (P < 0.05).