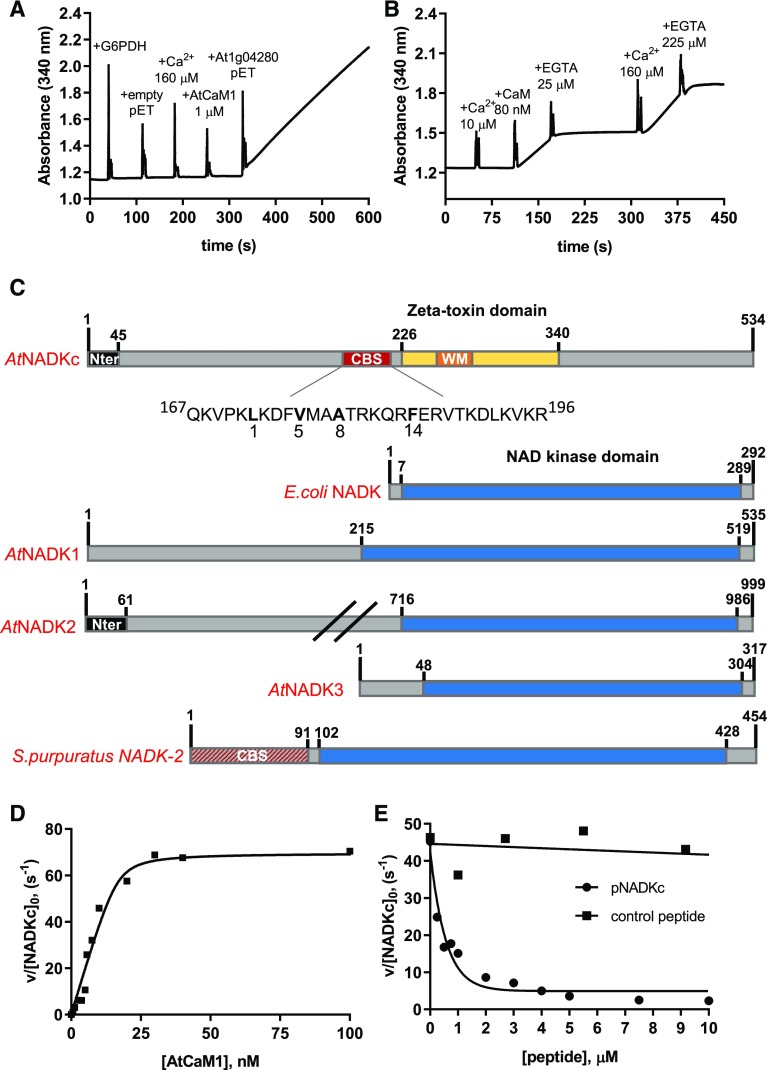
Figure 1.
Biochemical properties of a CaM-dependent NAD+ kinase identified in Arabidopsis. A, NAD+ kinase activity measured in an E. coli extract expressing an empty pET28b(+) and an E. coli extract expressing At1g04280. Spikes correspond to the moments of addition of Glc-6-P dehydrogenase (G6PDH), Ca2+, AtCaM1, and E. coli extracts (10 μg). B, NAD+ kinase activity in an E. coli bacterial extract expressing At1g04280. Ca2+, AtCaM1, and EGTA were added at different times, as indicated in the graph. C, Schematic representation of the NADKc primary sequence and comparison with previously known NAD+ kinases. Yellow, ζ-Toxin domain (InterPro homologous superfamily: IPR010488); black, N-terminal region with putative organelle target sequence; red, putative conserved type A 1-8-14 CaM-binding site (detailed below the scheme); orange, Walker A motif (WM; ATP-binding site); blue, NAD+ kinase domain (InterPro homologous superfamily: IPR016064); red/gray, N-terminal sequence expected to contain a CaM-binding site according to Love et al. (2015). Sequences used for comparison (UniProt) are as follows: E. coli NAD+ kinase, P0A7B3; Arabidopsis NAD+ kinases, AtNADK1, Q56YN3; AtNADK2, Q9C5W3; AtNADK3, Q500Y9; S. purpuratus NAD+ kinase-2 (sea urchin CaM-dependent NAD+ kinase; Love et al., 2015), C3RSF7. D, Affinity of NADKc recombinant protein for AtCaM1. Activity of the purified NADKc recombinant protein after denaturation in urea and subsequent refolding was measured in the presence of 50 μm Ca2+ and as a function of [AtCaM1]. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data shown are from one representative experiment. Binding data were analyzed assuming tight binding. The Kd value for AtCaM1 binding varied from 0.6 to 1 nm. E, Inhibition of NADKc activity by competition with the putative CaM-binding site (black circles). Black squares correspond to results obtained with a negative control peptide, which does not bind AtCaM1.