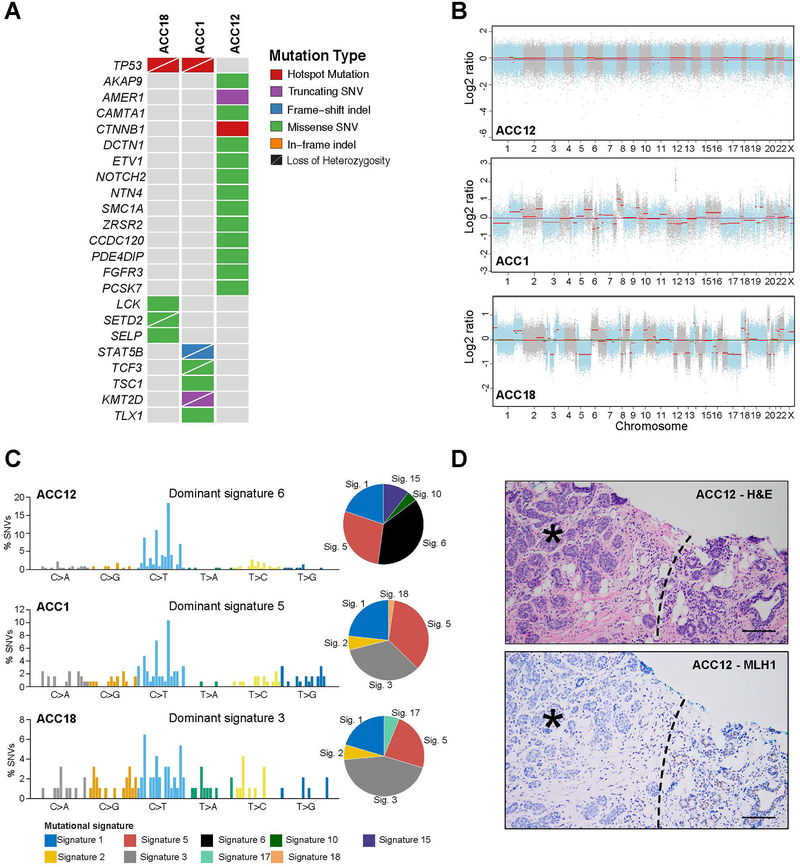
Figure 2. Repertoire of somatic mutations and mutational signatures of the acinic cell carcinomas of the breast.
(A) Non-synonymous somatic mutations affecting cancer-related genes13–15 and mutations shared among cases identified in the acinic cell carcinomas of the breast (ACCs; n=3) subjected to whole-exome sequencing (WES). Cases are shown in columns and genes in rows. (B) Copy number plots depicting segmented Log2 ratios (y-axis) plotted according to genomic position (x-axis). Chromosomes are demarcated by alternating blue and gray colors (C) Mutational signatures of all somatic SNVs in breast ACCs (n=3). Pie charts indicate the proportion of the different mutational signatures identified in each case. (D) Representative hematoxylin and eosin micrograph of ACC12 arising in a patient with an MLH1 germline mutation (top) and micrograph depicting loss of MLH1 expression in the tumor cells (*). Normal breast (right lower corner) shows retention of MLH1 expression. Dashed line Scale bar, 50 μm. SNV, single nucleotide variant. Sig, signature; SNV, single nucleotide variant.