Figure 1.
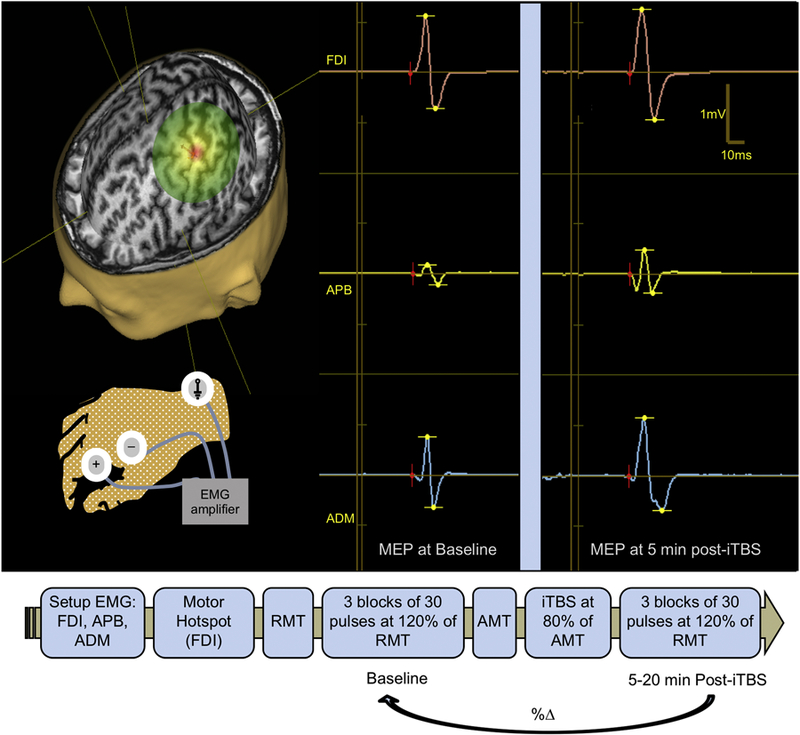
Top. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) assessments of cortical excitability—average amplitude of motor evoked potentials (MEPs) elicited by single-pulse TMS—and cortical plasticity—the change in excitability induced by intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS). (A) Magnetic Resonance (MR)-guided TMS was applied to the left primary motor cortex ‘‘hand knob” and resulting MEPs were recorded from the right first dorsal interosseous (FDI), abductor pollicis brevis (APB) and abductor digiti minimi (ADM) muscles by surface electromyography (EMG). (B) Example MEP traces before and after iTBS recorded from FDI, APB, and ADM. Bottom. Time-line of the study visit.
