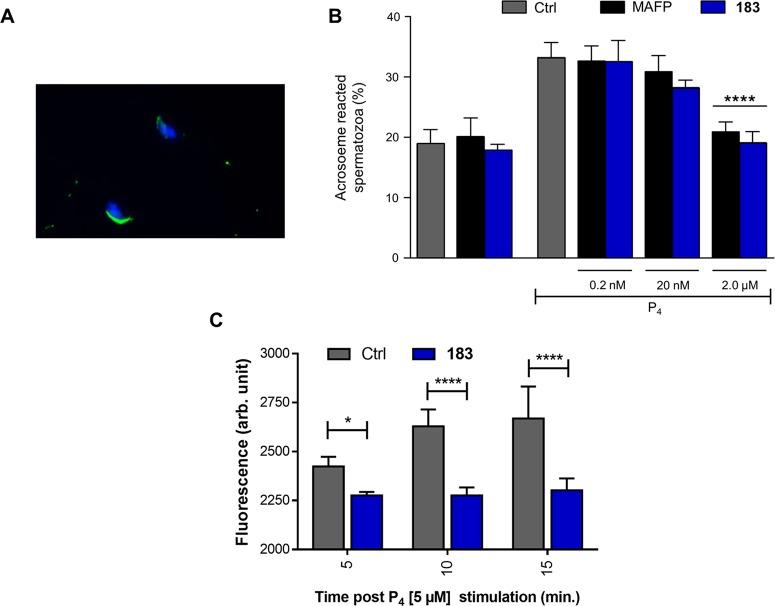
Figure 6.
(A) Representative image of one acrosome intact and one AR spermatozoa with the acrosomal enzymatic content and the nuclei stained with the PNA-FITC (green fluorescence) and DAPI (blue fluorescence), respectively. (B) Incidence of AR recorded on in vitro capacitated spermatozoa exposed to progesterone (P4:3 μM) in the absence (Ctrl) or presence of increasing concentrations of MAFP and 183 (from 0.2 nM to 2 μM). The induction of AR promoted by P4 was prevented in spermatozoa treated with 2 μM of MAFP or 183. In order to exclude any toxic effect, in vitro capacitated spermatozoa were also incubated with 2 μM of both the inhibitors (MAFP and 183 groups) without any treatment of P4. Data are expressed as mean with SD of n = 3 independent experiments. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Intracellular calcium analysis. Stimulation with P4 increases intracellular calcium levels in mouse spermatozoa as measured using Fluo-3 AM. 183 (2 μM) blocks the rise in intracellular calcium levels 5, 10, and 15 min after P4 stimulation. The data are expressed as florescence arbitrary units (Arb. Units) and are the mean ± standard deviation of three independent samples (full time course and positive control with ionomycin is given in SI Figure S9). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001