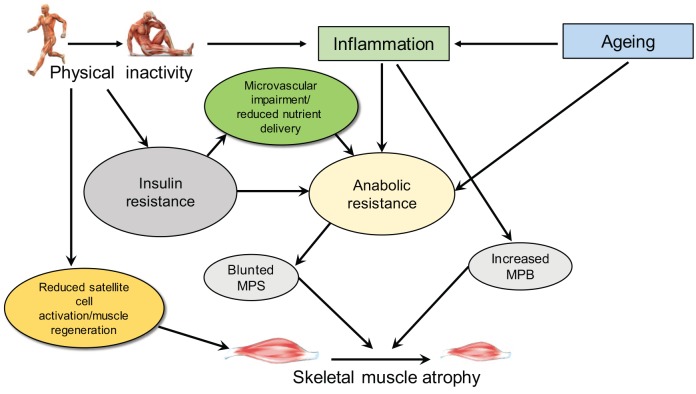
Figure 3.
A schematic to summarize the reported effects of physical inactivity on skeletal muscle atrophy. Physical inactivity and ageing have both been linked with increased inflammation and anabolic resistance; microvascular impairment also has a role due to insulin resistance; and with blunted MPS and increased MPB skeletal muscle atrophy is exacerbated. Physical inactivity can also cause reduced satellite cell activation, also linked to atrophy.
MPB, muscle protein breakdown; MPS, muscle protein synthesis.