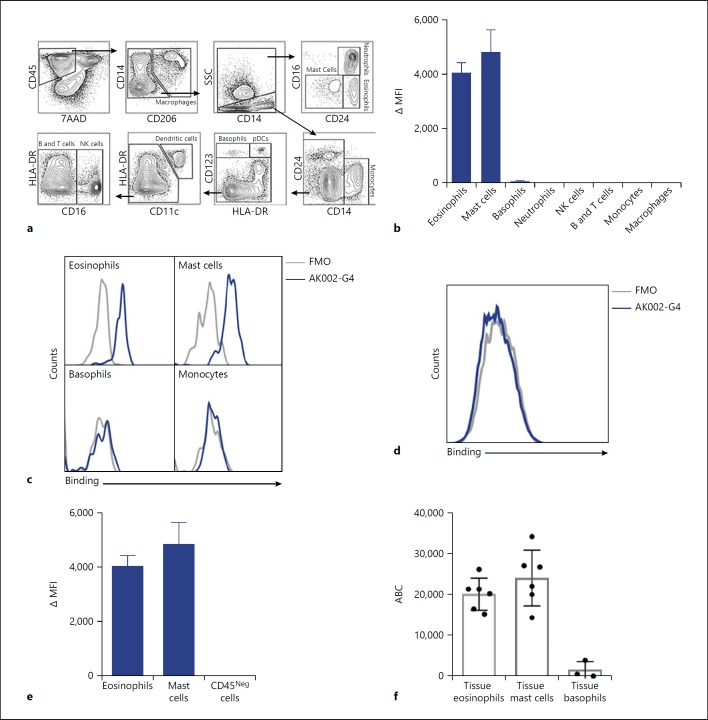
Fig. 3.
AK002-G4 selectively binds to eosinophils and mast cells from human tissue. a Flow cytometry gating strategy used to identify immune cell subtypes from human lung tissue. b AK002-G4 binding plotted as ΔMFI on immune cells identified using gating strategy in (a; Mean ± SD of 4 donors). c Representative histograms for eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, and monocytes stained with an FMO control (gray) or AK002-G4 (blue). d Representative histogram for viable CD45-negative cells in human lung tissue gated as shown above stained with an FMO control (gray) or AK002-G4 (blue). e AK002-G4 binding plotted as ΔMFI on eosinophils, mast cells and viable, CD45 negative cells in human lung tissue (mean ± SD of 4 donors). f Siglec-8 ABC of lung tissue eosinophils (median 21,529 ± 7,397), lung tissue mast cells (median 22,246 ± 7,929), and lung tissue basophils (median 621 ± 2,085) determined by quantitative cytometry (individual donors are plotted ± SD). ΔMFI was determined by subtracting the MFI for an FMO control sample from the MFI for cells stained with the conjugated antibody. ΔMFI values that were negative after subtracting the FMO were given a value of zero. MFI, median fluorescence intensity; FMO, fluorescence minus one; NK, natural killer; ABC, antibody binding capacity.