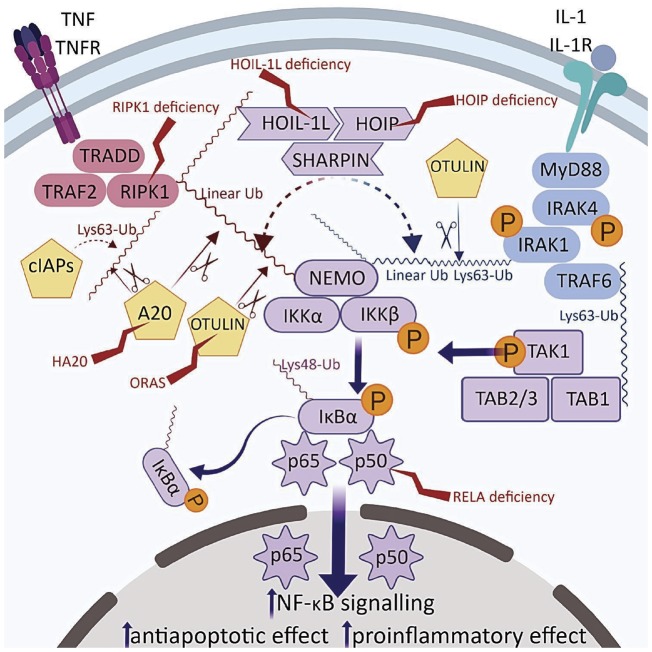
Fig. 1.
Disease-associated enzymes involving TNF and IL-1 pathways leading to NF-κB activation
Red proteins are involved in TNF and blue in IL-1 signalling. Purple indicates a shared pathway. Known relopathies marked with lightning symbol. Ubiquitin ligase activity indicated by dotted lines, deubiquitinase activity by scissor symbols. A20: TNF-induced protein 3; cIAPs: cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins; HOIL-1L: haem-oxidized IRP2 ubiquitin ligase 1L; HOIP: HOIL-1 interacting protein; IκBa: NF-κB inhibitor α; IKKα/b: inhibitor of NF-κB kinase a/b; IRAK 4/1: IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4/1; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary gene 88; NEMO: NF-κB essential modulator; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; OTULIN: ovarian tumor (OTU) deubiquitinase with linear linkage specificity; RIPK1: receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1; SHARPIN: SHANK-associated RH-domain-interacting protein; TAB1/2/3: TAK binding protein 1/2/3; TAK1: TGF-β activated kinase 1; TNFR: TNF receptor; TRADD: TNF receptor-associated death domain; TRAF2: TNF receptor-associated factor 2; TRAF6: TNFR-associated factor 6.