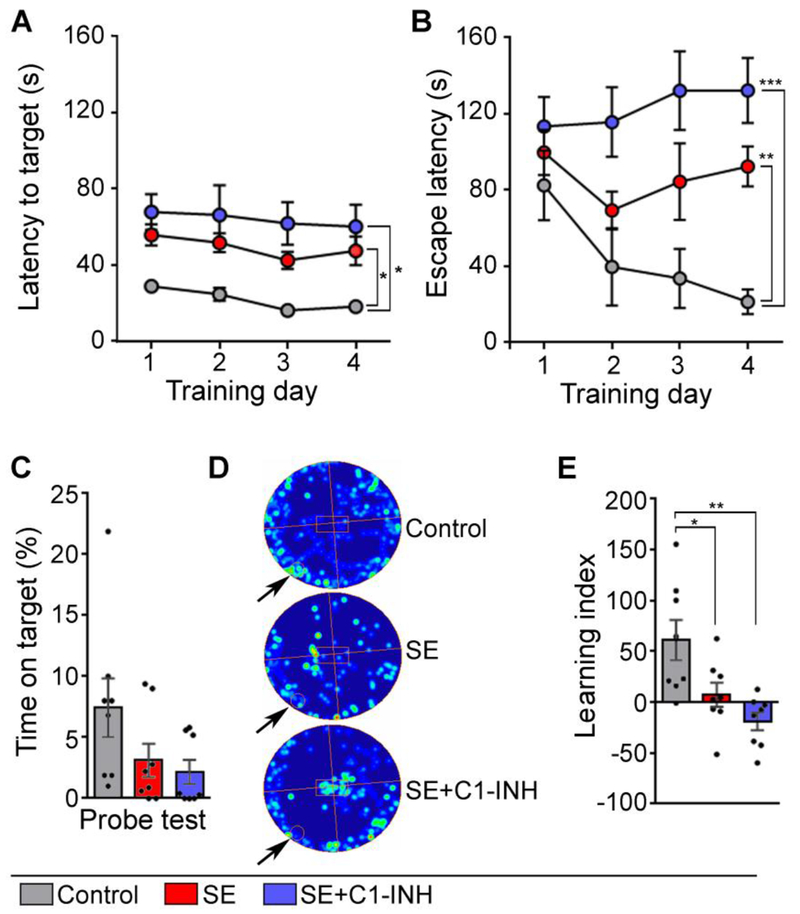
Figure 5.
Acute C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) treatment after status epilepticus (SE) does not attenuate deficits in hippocampal-dependent spatial learning and memory determined with the Barnes Maze (BM). BM was performed on days 17-21 after SE in control, SE, SE+C1-INH rats. (A-B) The graph shows the time to first reach (A) and to enter (B) the escape box on the BM platform (escape latency) during the training period (BM days 1-4; 4 trials/day). (C) The probe trial shows the percent of time spent over the covered escape box (target hole) (BM day 5). (D) Shows representative heat maps of rats’ movements during the probe trial for a control, SE, and SE+C1-INH rat (arrow points to the location of the target hole with escape box). (E) Learning index shows the difference in the escape latency between training days 1 and 4. Data are shown as mean +/− standard error of the mean. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 by repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. Controls, N=8; SE, N=8; SE+C1-INH, N=8.