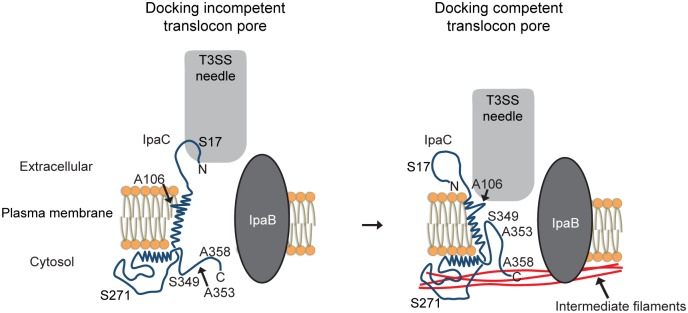
Fig 5. Model of conformational changes induced by interaction of IpaC with intermediate filaments.
The translocon pore is formed in the plasma membrane such that the N-terminal region is extracellular and that the C-terminal region is cytosolic [23]. In the absence of an interaction between IpaC and intermediate filaments, residues A106, S349, and A353 are not readily accessible from the extracellular space. Interaction of IpaC with intermediate filaments is associated with significantly greater extracellular accessibility of A106, S349, A353, and S17C. In contrast, IpaC interaction with intermediate filaments does not alter the accessibility of A358 or S271.