Figure 2.
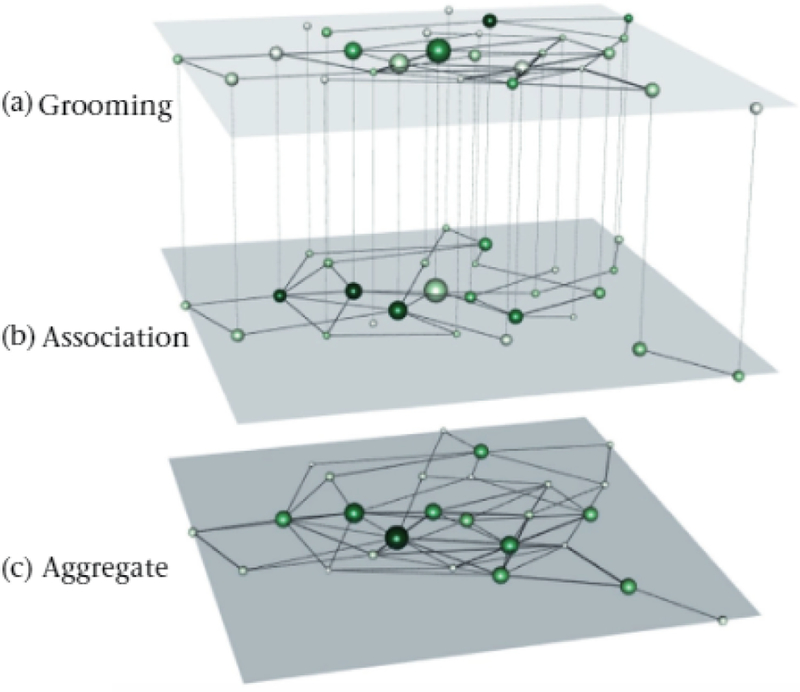
Social networks of a baboon group based oil (a) grooming interactions, (b) proximity-based association relations and (c) an aggregate or both interaction types. We created die network visualization using MuxViz (De Domenico, Porter. & Arenas, 2015). To construct a multilayer network, we joined die grooming and association monolayer networks as two layers in a multiplex network by connecting nodes that represent die same individual using interlayer edges. The sizes of the nodes are based on multilayer PageRank versatility (with larger nodes indicating larger versatilities). We colour die nodes based on monolayer PageRank centrality (with darker shades or green indicating larger values). A given individual in these two layers has die same size, but it can have different colours in the two layers. In the aggregate layer, we determine both the node sizes and their colours from PageRank centrality values in the aggregate network. We position the nodes in the same spatial location in die two layers and the aggregate network. The data (Franz el al., 2015a) are from Franz et al. (2015b).
