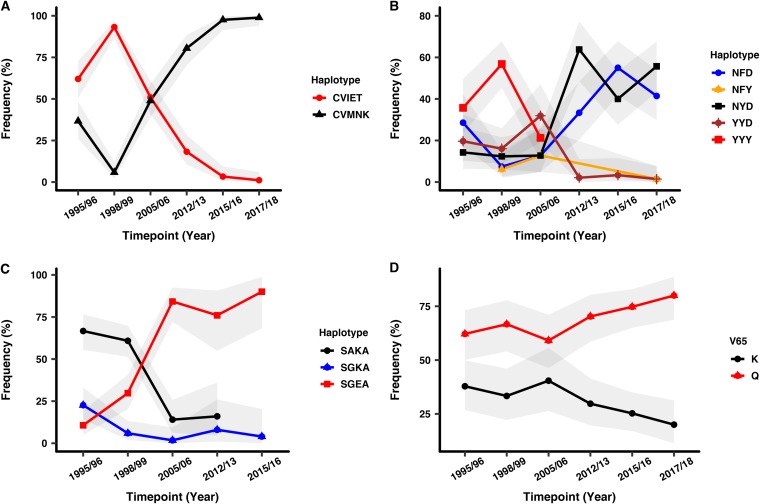
FIG 1.
crt, mdr1, and dhps haplotypes and nfs codon K65Q frequencies over time. (A) The crt-sensitive haplotype (CVMNK) decreased from 1995/1996 to 1998/1999 and increased onwards to almost fixation in 2017/2018, while the crt-resistant haplotype (CVIET) followed an opposite pattern. (B) The 3D7 mdr1 haplotype NYD had was the least prevalent in comparison to the mutant haplotypes NFD, YYD, and YYY pre-ACT introduction. The triple-mutant YYY was undetectable after 2005/2006, while the 3D7 NYD and mutant NFD haplotypes started to increase in the population after 2005/2006. The mutant YYD and NFY haplotypes decreased to almost zero in 2017/2018. (C) The SP-sensitive haplotype (SAKA) was on a decline from 1995/1996 and was undetectable in the population after 2012/2013. The SP-resistant double-mutant haplotype SGEA was on the increase from 1995/1996 and reached >80% frequency in 2015/2016. The single-mutant haplotype SGKA was the least prevalent throughout the sampling period. (D) The two nfs K65Q alleles appear to have stable frequencies from 1995/1996 to 2005/2006, but the frequency of K65 starts to drop after 2005/2006, while that of 65K starts to increase after 2005/2006. In gray are the 95% confidence intervals.