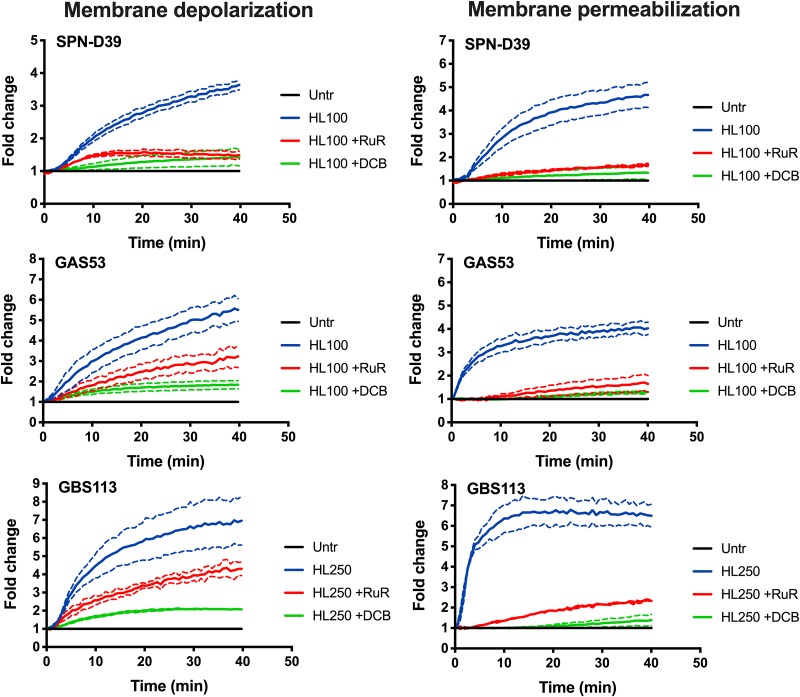
FIG 3.
Inhibition of membrane depolarization and permeabilization by calcium and sodium transport inhibitors. Bacteria were grown in THY, washed, and resuspended in PBS with 25 mM glucose to energize the cells. DiBAC4(3) and propidium iodide were added to the bacterial suspension, and the cells were allowed to equilibrate for 40 min at 37°C before the experiment was started. At 0 min, the bacterial cells were pretreated with inhibitors (30 μM [final concentration] ruthenium red [RuR] and 25 μM [final concentration] dichlorobenzamil [DCB]), after which 100 μg/ml (6 μM; for SPN-D39 and GAS strains) and 250 μg/ml (15 μM; for GBS) of HAMLET was added. The samples were immediately read in a fluorescence plate reader every 30 s for 40 min. (Left panels) Membrane polarity was measured using a 485/20-nm excitation and 528/20-nm emission filter combination, and depolarization of the membrane was detected through increased DiBAC4(3) fluorescence over time. (Right panels) Membrane integrity was recorded using a 528/20-nm excitation and 605/20-nm emission filter, and membrane disruption was detected through an increased propidium (PI) fluorescence intensity over time. The graphs show the average of results from 3 experiments for each strain as a solid line, with dashed lines of the same color representing the standard deviation.