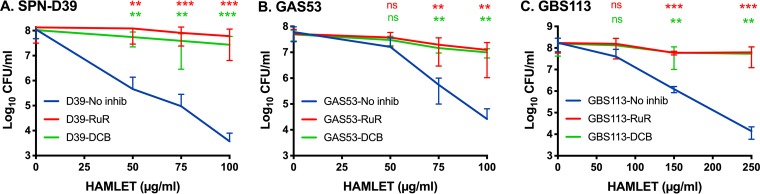
FIG 4.
Inhibition of HAMLET-induced death. Bacteria were grown in THY and washed and resuspended in PBS with 25 mM glucose to keep the bacteria energized. The bacterial suspensions were prepared to obtain a starting concentration of approximately 1 × 108 CFU/ml. The bacteria were preincubated for 5 min at 37°C in the presence or absence of ruthenium red (RuR; 30 μM; red line) or dichlorobenzamil (DCB; 25 μM; green line). Then, increasing concentrations of HAMLET were added to wells of each bacterial strain, and the bacteria were allowed to incubate for 1 h at 37°C. Bacteria were then serially diluted, dilutions were plated onto agar, and colonies were allowed to grow for 24 to 48 h. Viable CFU were counted, and the concentration in numbers of CFU per milliliter was calculated and is depicted in the graphs. (A) S. pneumoniae D39, (B) GAS 53, and (C) GBS 113. The results represent the mean data from at least 5 separate experiments, with standard deviations. Statistical comparison of groups was performed using Welch’s ANOVA, with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test used for comparisons of individual groups. P values are presented from Dunnett’s comparison of experiments with no inhibitor (No inhib) versus RuR (red asterisks) and no inhibitor versus DCB (green asterisks). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, no significant difference.