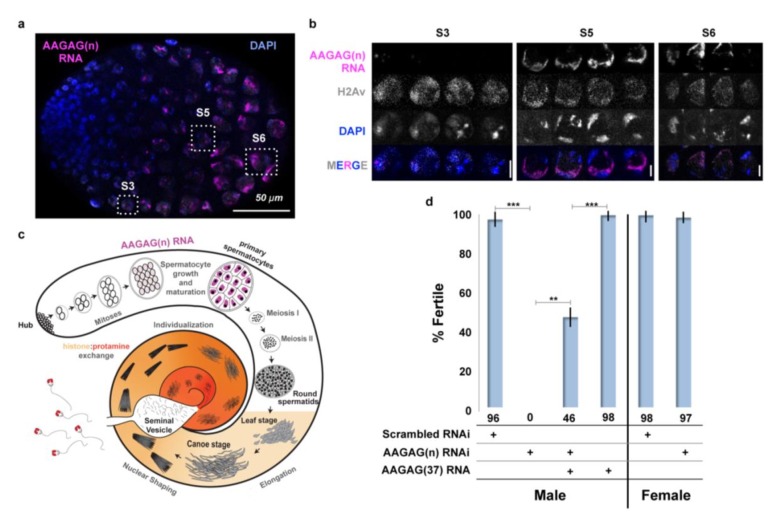
Figure 2. AAGAG RNA is enriched in primary spermatocytes and necessary for male fertility.
(a) Confocal section of a larval testis. RNA-FISH to AAGAG = magenta, H2Av (chromatin) IF = gray, DNA (DAPI) = blue. S3, S5, and S6 refer to primary spermatocyte stages. (b) Enlarged confocal sections (representative boxes in a) of spermatocyte stages in larvae testes; scale bars = 5 µm. (c) Schematic summary of AAGAG RNA (magenta) localization in adult testes (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for a detailed description of spermatogenesis stages and events). AAGAG RNAs are visible in 16 cell primary spermatocytes (dark pink), and potentially 16 cell spermatogonial cysts (light pink); no AAGAG RNA was detected at earlier stages (hub, 2–8 cell spermatogonial cysts) or after the primary spermatocyte stage (meiosis I and II, sperm elongation- which includes leaf, canoe, individualization steps, and maturation). Post-round spermatid stages are indicated as spermatid nuclei. (d) Fertility after depletion of AAGAG(n) RNA in male primary spermatocytes or female ovaries using the Bam-GAL4 driver. An ~72% reduction in AAGAG RNA levels in testes (see Figure 2—figure supplement 3, B and C) results in complete male sterility but has no effect on female fertility. Expression of AAGAG(37) RNA simultaneously with AAGAG RNAi (both driven by Bam-Gal4) partially rescues male sterility (46% fertile). Expression of AAGAG RNA alone, without depletion of endogenous AAGAG RNAs, has no impact on male fertility. Statistically significant differences based on T-tests (two tailed, type three) are indicated by horizontal lines; ***p<0.001, **p<0.01; variation is represented by stdev.