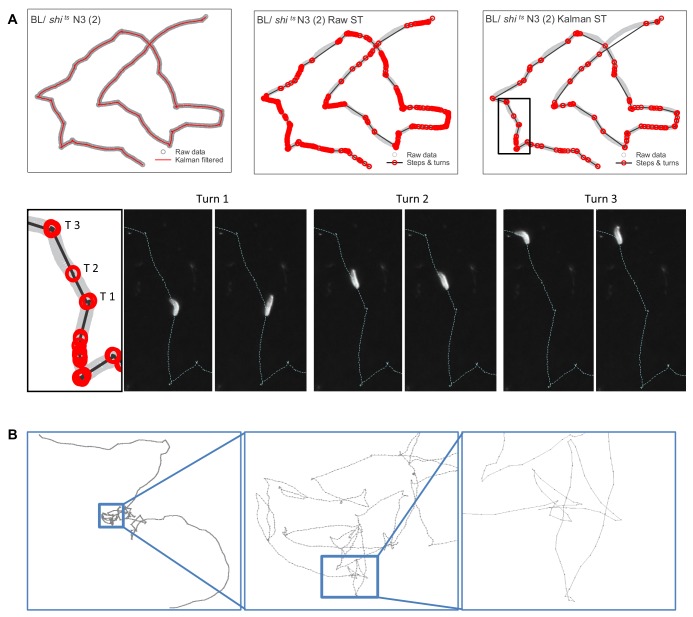
Figure 2. Estimating move step lengths in Drosophila larva tracks across broad scales.
(A) Examples of track processing and turn identification. Row 1, column one shows an example of the effect of the Kalman filter on raw track data; column two shows the steps and turns that would result if raw track data were analysed; column three shows the steps and turns identified following the Kalman smoothing of the raw data. Row two shows the turns executed by the larva for a short section of the track. Note that the method detects small (turn 2, (T2) and large turns (turn 1 and 3 (T1, T3)). (B) Example of normal substrate exploration (control BL / + larva) shows a similar pattern of complexity at all scales, characteristic of scale-invariant Lévy walk patterns.
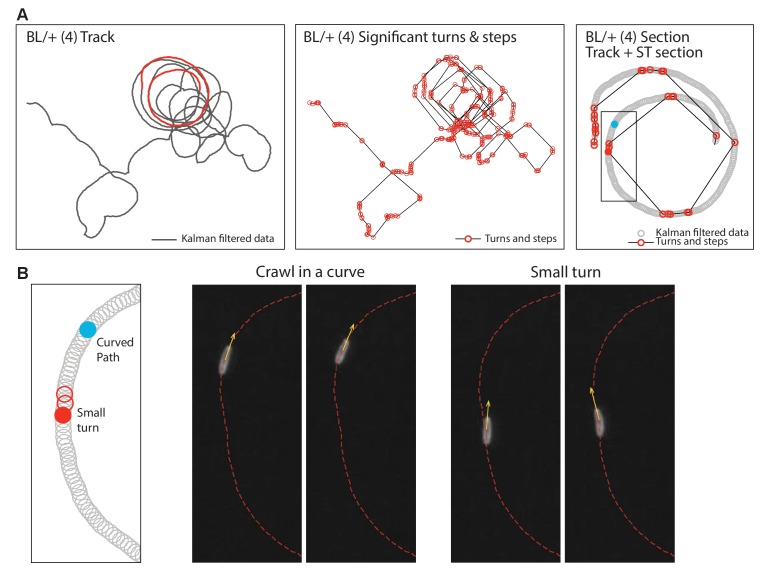
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Analysis of curved paths.
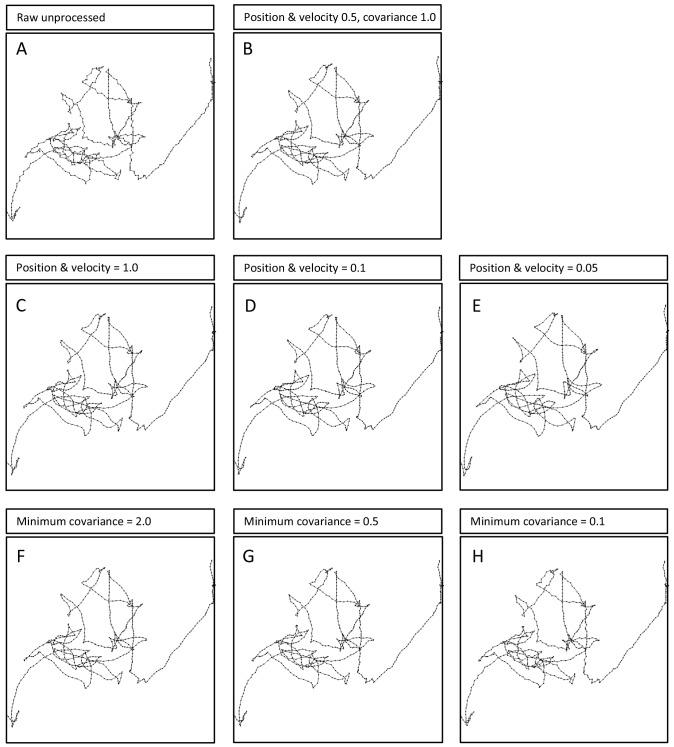
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Effects of Kalman filter parameter changes on an example larva track.
Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Effect of edge collision on search strategy.