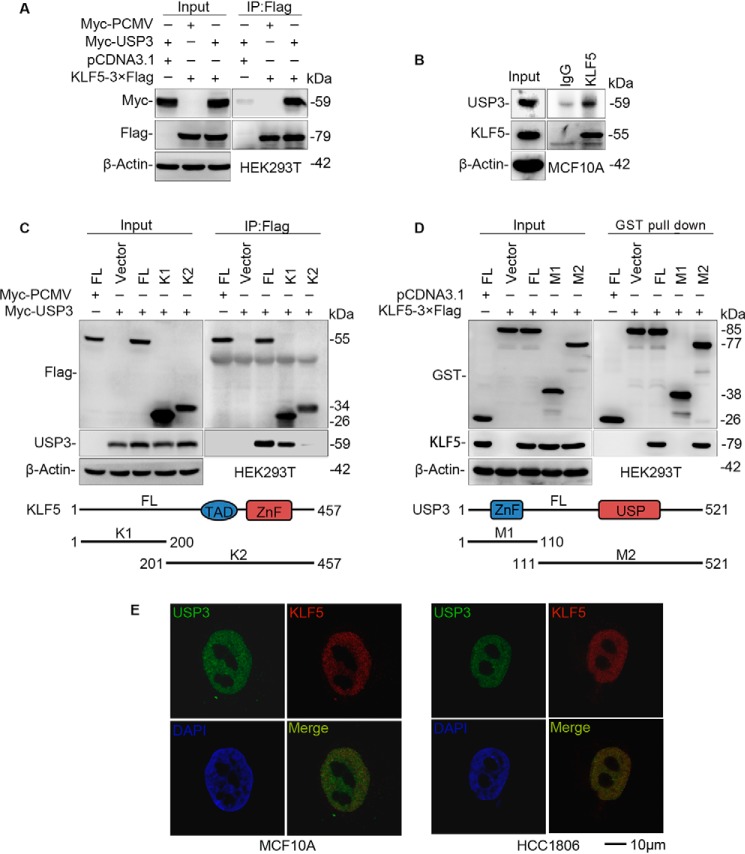
Figure 3.
USP3 interacts with KLF5. A, exogenous USP3 and KLF5 proteins interact with each other in HEK293T cells. Myc-USP3 and KLF5–3×FLAG were co-expressed in HEK293T cells. KLF5–3×FLAG was immunoprecipitated by FLAG-M2 beads. The experiment was repeated three times, and a representative result is shown. B, endogenous USP3 and KLF5 proteins interact with each other in MCF10A cells. Endogenous USP3 and KLF5 proteins were immunoprecipitated with the anti-KLF5 antibody. IgG serves as the negative control. The experiment was repeated three times, and a representative result is shown. C, mapping the KLF5 domain that interacts with USP3. FLAG-tagged full-length or mutants of KLF5 (a schematic diagram is shown below the panel) and Myc-USP3 were cotransfected into HEK293T cells. Immunoprecipitation was performed with FLAG-M2 beads. The experiment was repeated three times, and a representative result is shown. D, mapping the USP3 domain that interacts with KLF5. GST-tagged full-length or mutants of USP3 (a schematic diagram is shown below the panel) and KLF5–3×FLAG were cotransfected into HEK293T cells. Immunoprecipitation was performed with GSH beads. The experiment was repeated three times, and a representative result is shown. E, endogenous USP3 and KLF5 are co-localized within the nuclei of HCC1806 and MCF10A cells. Immunofluorescence staining was used to detect the subcellular location of USP3 and KLF5. 4,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole was used to stain the DNA. Scale bar, 10 μm. Endogenous USP3 and KLF5 are co-localized in the nuclei of all nonmitosis cells, and only representative results are shown. IP, immunoprecipitation.