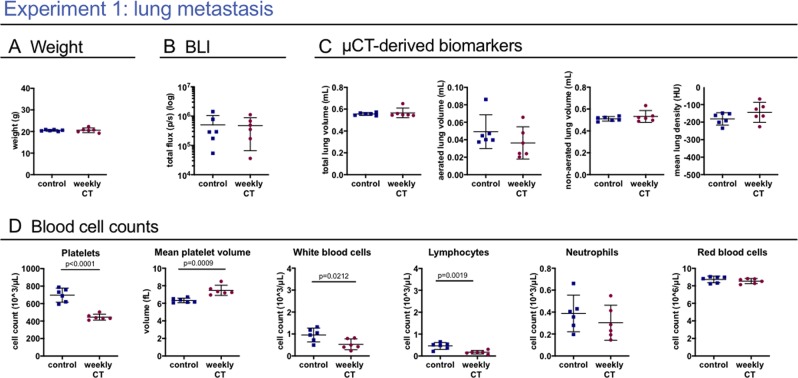
Figure 2.
Weekly low-dose 4D μCT does not influence the general health and disease outcomes but induces a sub-clinical decrease in white blood cell and platelet counts in a murine metastasis model. Experiment 1: weekly low-dose 4D µCT scanning of metastasis-bearing mice induces a decrease in circulating platelets, increase in mean platelet volume, decrease in red blood cells and absolute white blood cell count, due to a decrease in number of lymphocytes. (A) Mouse body weight at end point. (B) In vivo BLI signal intensity expressed as total flux (p/s) from the lung, measuring metastatic load. (C) µCT-derived biomarkers (total lung volume, aerated lung volume, non-aerated lung volume and mean lung density). (D) Selected blood cell parameters: absolute platelet cell count, mean platelet volume, white blood cell count, lymphocyte count and neutrophil count and red blood cell count. Data are presented as individual values, group mean and 95% confidence intervals. P-values are presented in the graph when p < 0.05. HU, Hounsfield units.