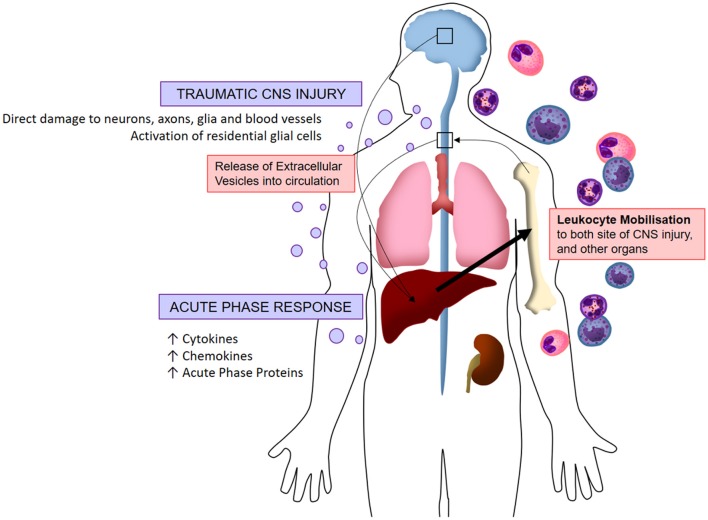
Figure 2.
Visualized hypothesis of EV-mediated systemic inflammation response to traumatic CNS injury. Acute traumatic injuries to the brain and spinal cord induce the release of extracellular vesicles into circulation. These EVs localize to peripheral organs whereby they induce the production of pro-inflammatory molecules (chemokines, cytokines, acute phase proteins), in turn stimulating the mobilization of leukocytes which infiltrate both the CNS and peripheral organs. This systemic immune response is referred to as the acute phase response.