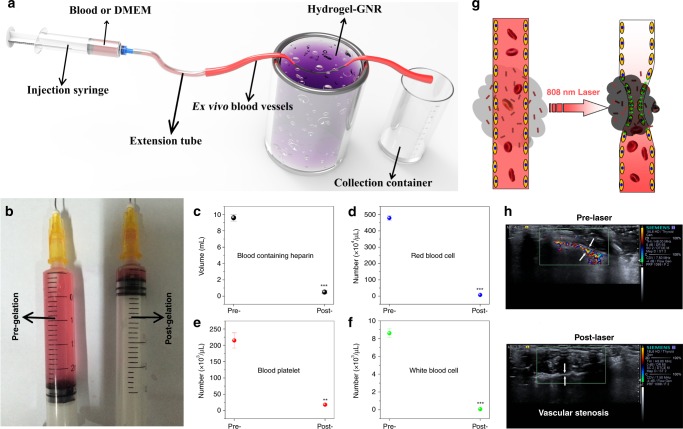
Fig. 3.
Occlusion tests of blood supply on ex vivo and in vivo artery model. a Experimental apparatus schematic available for evaluating the occlusion outcome of ex vivo blood vessels with an inner diameter of 1.00 mm based on the extravascular gelation shrinkage-induced internal stress for squeezing blood vessels. b Traversed volume of DMEM through the ex vivo blood vessels before (left) and after (right) gelation of hydrogel–GNR. c, f Collected blood volume (c), red blood cells (d), blood platelet (e), and white blood cells (f) traversed through ex vivo blood vessels using rabbit blood containing heparin instead of above DMEM. Data are expressed as mean value ± SD (n = 3). **P ˂ 0.01 and ***P ˂ 0.001, and the statistical significances were obtained using student's t test in comparison to Pre-gelation. g In vivo schematic of extravascular gelation shrinkage-induced internal stress for squeezing blood vessels upon exposure to 808 nm laser. h CDFI images of abdomen artery of nude mice around which hydrogel–GNR solution was administrated, and in particular, CDFI images were captured before and after 808 nm laser irradiation, respectively, wherein white arrows indicate the blood vessels of abdomen artery.