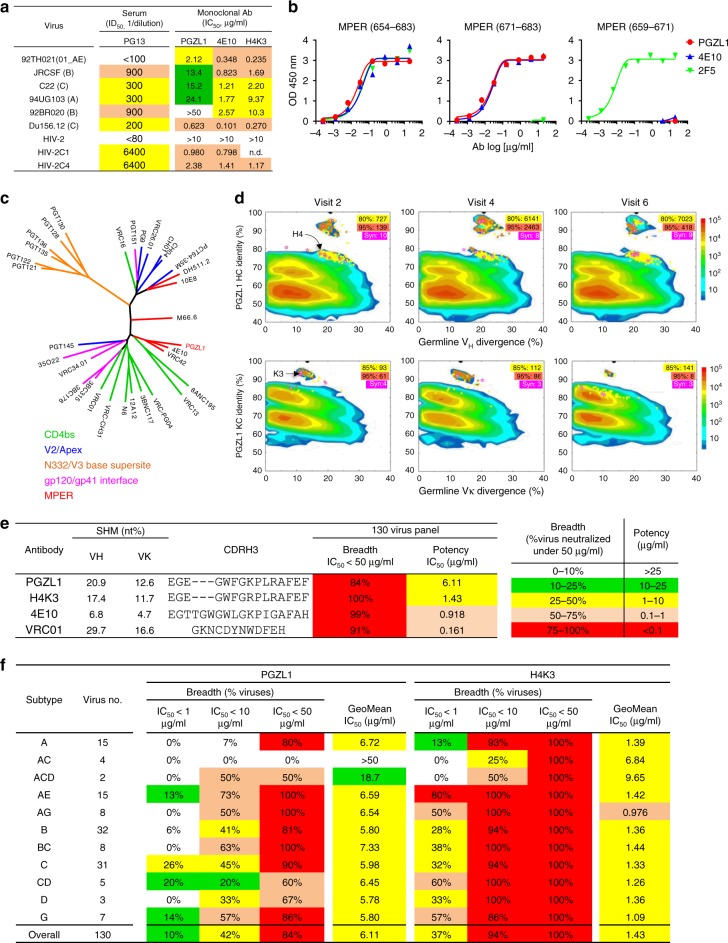
Fig. 1.
Properties of an MPER-targeted bnAb. a Neutralization of HIV-1 six-virus panel and HIV-2 (HIV-1 MPER) chimeras by PG13 plasma and monoclonal antibodies PGZL1, 4E10, and H4K3. b ELISA binding of PGZL1 to MPER peptides, using 4E10 and 2F5 as controls. c Maximum likelihood (ML) tree of HC variable regions of described bnAbs, colored by Env specificity. d Divergence/identity analysis of donor PG13 antibody repertoire over three visits in 9 months. NGS-derived antibody chains are plotted as a function of sequence identity to PGZL1 and divergence from their putative germline genes. Colors indicate sequence density. Sequences with a CDR3 identity of ≥80/85% (HC/KC) and with a CDR3 identity of ≥95% are shown as yellow and orange dots on the 2D plots, with the number of sequences highlighted in yellow and orange shades, respectively. Sequences bioinformatically selected for synthesis are shown as magenta stars on the 2D plots, with the number of sequences (Syn) highlighted in magenta shade. e, f Neutralization breadth and potency of PGZL1 and H4K3 against a 130-virus panel (e) and the same data as in e but subdivided by HIV subtype (f).