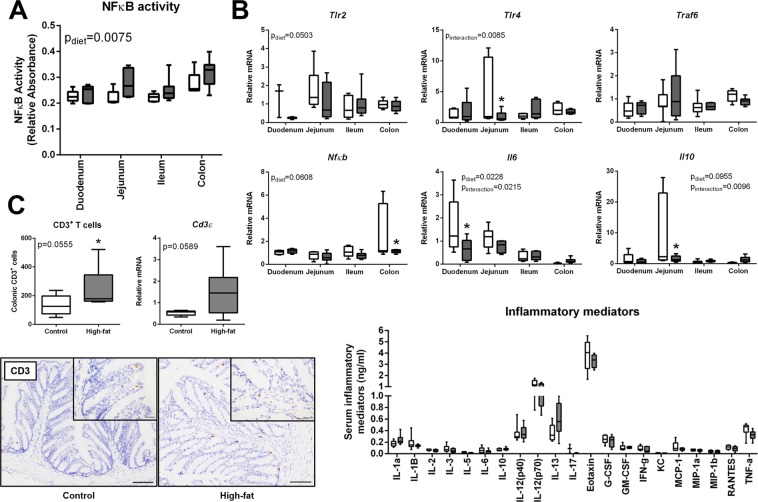
Figure 4.
mDIO is associated with increased maternal intestinal NFκB activity and an increased number of colonic CD3+ T cells. (A) NFκB activity in the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and colon tissue in control and high-fat dams. (B) Relative transcript levels of Tlr2, Tlr4, Traf6, Nfκb, Il6, and Il10 in control and high-fat fed dams. (C) Number of colonic CD3+ T cells in control (open bars, n = 6) and high-fat (grey bars, n = 7) dams and relative transcript levels of colonic CD3ε in control and high-fat dams. Representative images of CD3 T cell immuno-localization in the colon of control and high-fat dams. Scale bar represents 100 µm. Maternal serum eotaxin, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-12 (p40), IL-12 (p70), IL-13, IL-17A, KC, MCP-1, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, RANTES, and TNF in control and high-fat fed dams. Main effects are written as text in the figure. Data were analyzed with a 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc multiple comparisons or Student’s t-test where appropriate. Control: open boxes, (n = 7) and high-fat: grey boxes, (n = 9). *p < 0.05.