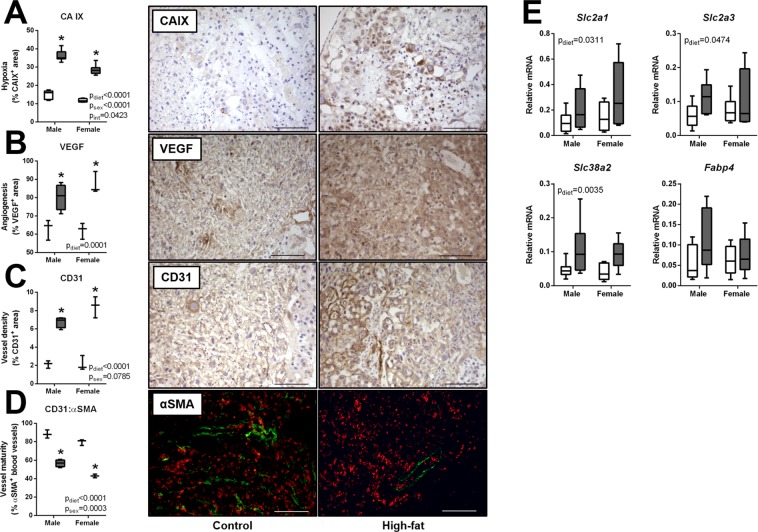
Figure 6.
mDIO promotes placental hypoxia and angiogenesis, and alters nutrient transporters. Images represent immuno-localization of CAIX, VEGF and CD31 (brown staining) in control and high-fat dams. Scale bars represent 100 µm. (A) Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) results from computerized image analysis of CAIX immunostaining in placentae of control (open bars, n = 3) and high-fat (grey bars, n = 4) dams. (B) Vascular endothelial growth factor results from computerized image analysis of VEGF immunostaining (open bars, n = 3) and high-fat (grey bars, n = 4) dams. (C) Cluster of differentiation (CD31) results from computerized image analysis of CD31 immunostaining in placentae of control (open bars, n = 3) and high-fat (grey bars, n = 4) dams. (D) Ratio of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) to CD31 in placentae of control (open bars, n = 3) and high-fat (grey bars, n = 4) dams and representative images of α-SMA (green) pericytes lining CD31 (red) endothelial cells (E) Relative mRNA levels of glucose transporter 1 (Slc2a1), glucose transporter 3 (Slc2a3), system N/A amino acid transporter 2 (Slc38a2), and fatty acid binding protein 4 (Fabp4) in placentae of control and high-fat dams Control: open boxes, (n = 7) and high-fat: grey boxes, (n = 9). *p < 0.05.