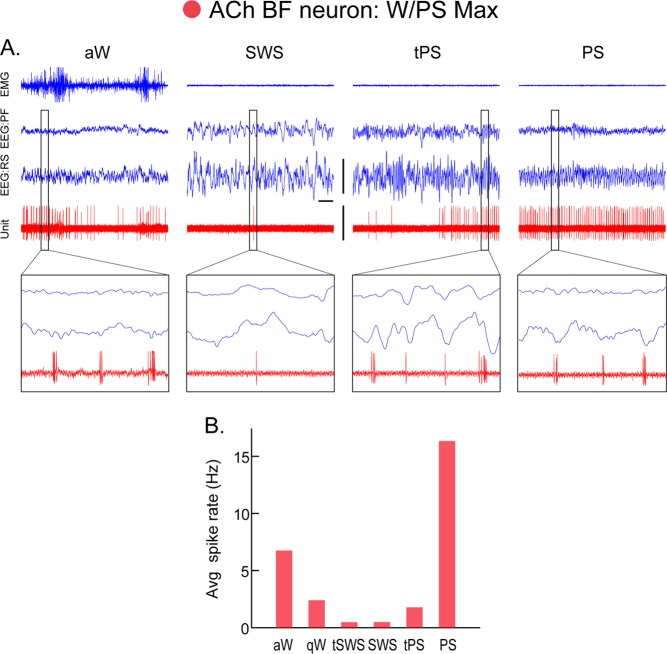
Fig. 4.
Discharge of an acetylcholine (ACh) basal forebrain (BF) neuron across sleep-wake states. A Record of a neuron labeled by juxtacellular technique with Neurobiotin (Nb) and identified by immunohistochemistry for choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) as cholinergic in the magnocellular preoptic nucleus (MCPO) of the rat. As evident in 10 s traces (above), the unit fired during aW, virtually ceased firing during SWS, resumed firing during tPS, and discharged maximally during PS. As evident in expanded 0.5 s traces (below), the unit discharged in rhythmic bursts of spikes with theta EEG activity that was present intermittently during periods of aW, toward the end of tPS and continuously during PS. B Average discharge rate (Hz) across the sleep-wake states and transitions (t) of the same cell. Avg, average; aW, active wake; EEG, electroencephalogram; EMG, electromyogram; PF, prefrontal cortex; PS, paradoxical sleep; qW, quiet wake; RS, retrosplenial cortex; SWS, slow wave sleep; tPS, transition to PS; tSWS transition to SWS. Bar for horizontal scale: 1 s. Bar for vertical scales: 1 mV for EEG/EMG and 1.5 mV for Unit. (Reprinted with permission from Lee et al. [69])