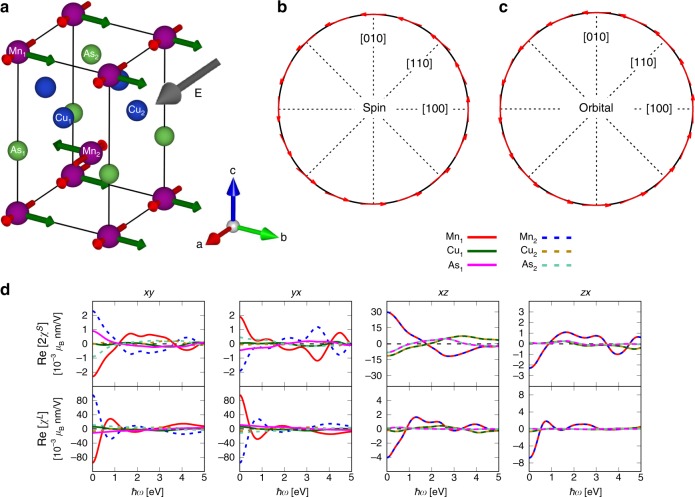
Fig. 2.
Rashba-Edelstein effect in CuMnAs with magnetic moments along the a-axis. a Sketch of the tetragonal unit cell of CuMnAs. The red arrows on the Mn atoms represent the initial magnetic moments. Applying an electric field along the (100) direction (gray arrow) induces a nonequilibrium magnetization mainly along the (010) direction (green arrows). b In-plane symmetry of the induced spin magnetization as a function of the static electric-field direction for Mn. c In-plane symmetry of the induced orbital magnetization as a function of the static electric-field direction for Mn. d Real parts of the nonzero components ( x, y, or z) of the spin and orbital Rashba-Edelstein susceptibility tensors, and , as function of the driving electric-field frequency, .