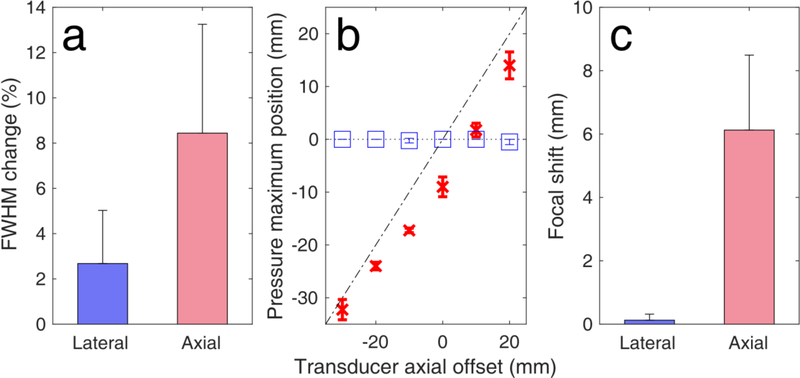
Fig. 5 :
Simulated human skull-induced focal distortion. (a) Full width at half maximum (FHWM) change due to the presence of the human skull. FWHM changes were first averaged across the pulse lengths for each axial offset (n = 4 pulse lengths), and then averaged across all depths (n=6 axial offsets). (b) Simulated focal shifts along the axial (red crosses) and lateral (blue boxes) dimensions. Diagonal dotted-dashed line and parallel dotted line denote axial and lateral shifts equal to zero, respectively (n=4 pulse lengths). (c) Average focal shifts across the lateral and axial dimensions (n=6 axial offsets). Data presented as mean ± standard deviation.