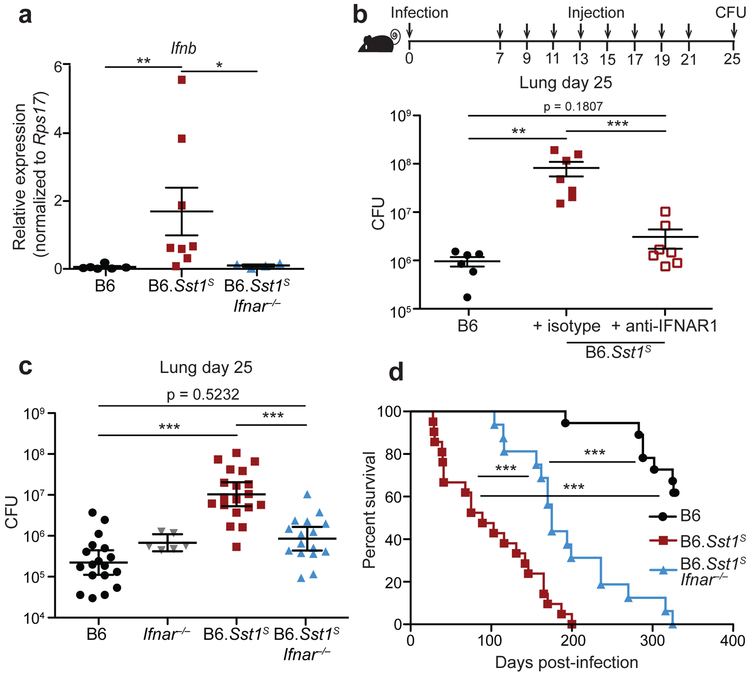
Fig. 1 ∣. Type I IFN drives enhanced susceptibility of B6.Sst1S mice.
a, Expression of Ifnb in Mtb-infected lungs at day 25, measured by quantitative RT-PCR, normalized to Rps17. b, Lung bacterial burdens at day 25 from Mtb-infected mice treated with anti-IFNAR1 or isotype control antibody. c, Lung bacterial burdens at day 25, or d, survival, of Mtb-infected mice. c-d, Combined results from three independent infections. Sample size n: B6 = 6, B6.Sst1S = 8, B6.Sst1SIfnar−/− = 4 (a); B6 = 6, isotype = 7, anti-IFNAR1 = 7 (b); B6 = 18, Ifnar−/− = 6, B6.Sst1S = 19, B6.Sst1SIfnar−/− = 16 (c); B6 = 18, B6.Sst1S = 21, B6.Sst1SIfnar−/− = 16 (d). For a-d, all except B6 mice were bred in-house. Center and error bars show mean and SEM. Analyzed with two-ended Mann-Whitney test (a-c) or two-ended Log-rank test (d). Asterisk, p ≤ 0.05; two asterisks, p ≤ 0.01; three asterisks, p ≤ 0.001.