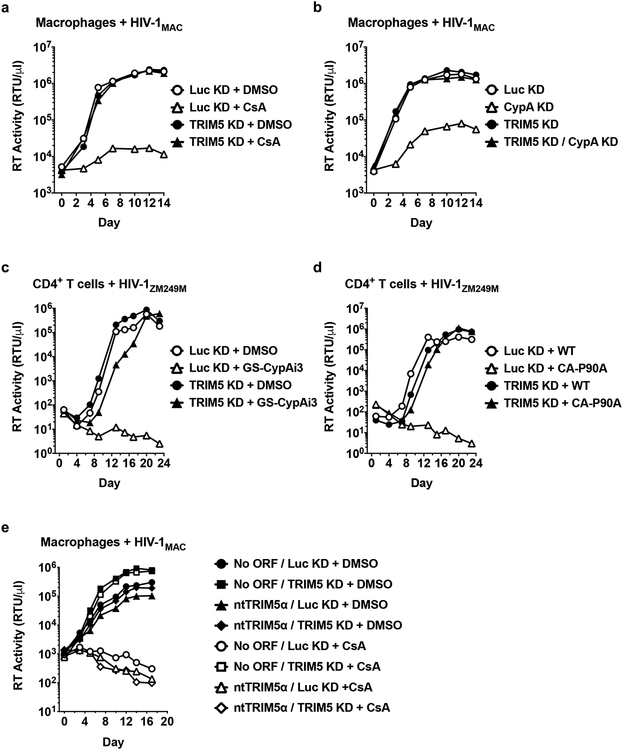
Fig. 4. Endogenous TRIM5α suppresses spreading infection of HIV-1 in primary human macrophages and CD4+ T cells when the CA-CypA interaction is disrupted.
a and b, Spreading infection of HIV-1MAC in TRIM5 or Luc knockdown macrophages with 5 μM CsA (a) or with vectors bearing shRNAs targeting CypA or Luc (b), as indicated. c and d, Spreading infection of HIV-1ZM249M in CD4+ T cells expressing shRNA targeting TRIM5 or Luc with 2.5 μM GS-CypAi3 (c) or when challenged with virus bearing CA-P90A (d), as indicated. e, Spreading infection of HIV-1MAC in macrophages transduced with all-in-one shRNA-rescue lentivectors described in Fig. 2, as indicated. HIV-1 replication was monitored by measuring reverse transcriptase (RT) activity in the culture supernatant over time. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments using cells from two blood donors for each condition.