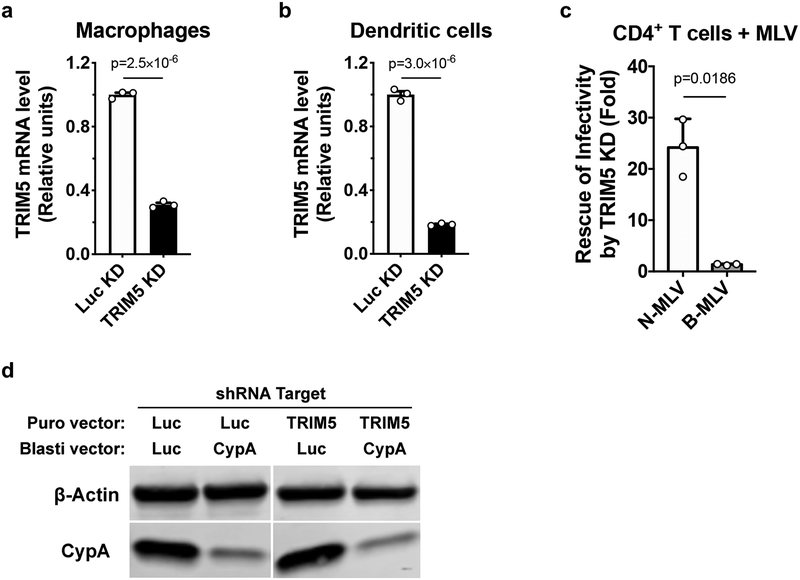
Extended Data Fig. 2. Assessment of shRNA-mediated knockdown in primary human blood cells.
a-c, Lentiviral vectors containing puromycin N- acetyltransferase (PuroR) and shRNA targeting TRIM5 or Luc were used to transduce macrophages (a), dendritic cells (b), or CD4+ T cells (c). At 3 days post-transduction, cells were selected with puromycin for 3 days. Total RNA was isolated from the macrophages and dendritic cells, followed by cDNA synthesis, and qPCR with TaqMan detection of TRIM5 and the housekeeping gene OAZ1, for normalization (mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent samples). Significance was determined by two-tailed, unpaired t-test (a and b). The selected CD4+ T cells were challenged with N- or B-MLV vector harboring GFP reporter for 3 days. Flow cytometry was used to assess the percentage of GFP+ cells. The infectivity of each vector in TRIM5 knockdown cells was normalized to the Luc control condition. Shown is mean ± SD (n = 3 donors for each). Significance was determined by two-tailed, paired t-test (c). d. Macrophages were simultaneously transduced with two lentiviral vectors, the first expressing shRNA targeting TRIM5 or Luc with PuroR, and the second expressing shRNA targeting CypA or Luc with blasticidin S-deaminase (bsd). After selection with both antibiotics, CypA and β-actin proteins were detected by western blot. Data shown is representative of three independent experiments using cells from three blood donors.