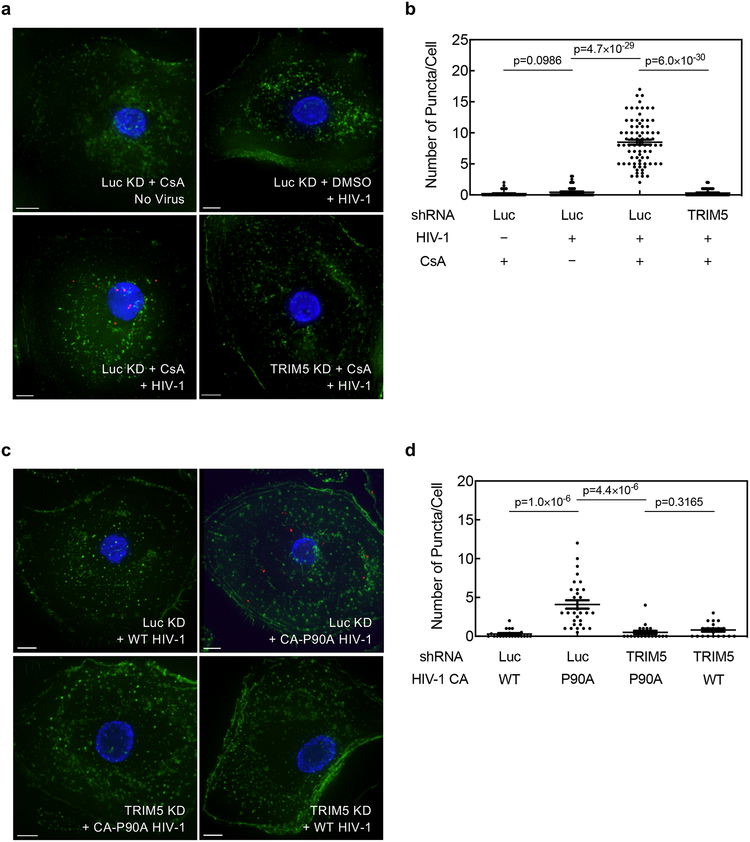
Extended Data Fig. 5. CA-CypA interaction prevents association of endogenous TRIM5α with HIV-1 CA in primary human macrophages.
a-d, TRIM5 or Luc knockdown macrophages from a different blood donor than that used in Fig. 4 were challenged with VSV G-pseudotyped, HIV-1NL4–3GFP in the presence of 5 µM CsA or DMSO solvent for 2 hrs (a and b), or challenged with HIV-1NL4–3GFP bearing WT CA or CA-P90A (c and d). PLA was then performed using anti-CA (p24) and anti-TRIM5α antibodies. Representative images (a and c) show PLA puncta (red), nuclei stained with Hoechst (blue), and actin filaments stained with phalloidin (green). The plots (b and d) are the number of PLA puncta per cell in the PLA with mean ± SEM. b, Luc KD + CsA No Virus, n = 45 cells analyzed; Luc KD + DMSO + HIV-1, n = 45; Luc KD + CsA + HIV-1, n = 80; TRIM5 KD + CsA + HIV-1, n = 45. d, Luc KD + WT HIV-1, n = 20; Luc KD + CA-P90A HIV-1, n = 30; TRIM5 KD + CA-P90A HIV-1, n = 20; TRIM5 KD + WT HIV-1, n = 20. Significance was determined by two-tailed, unpaired t-test.