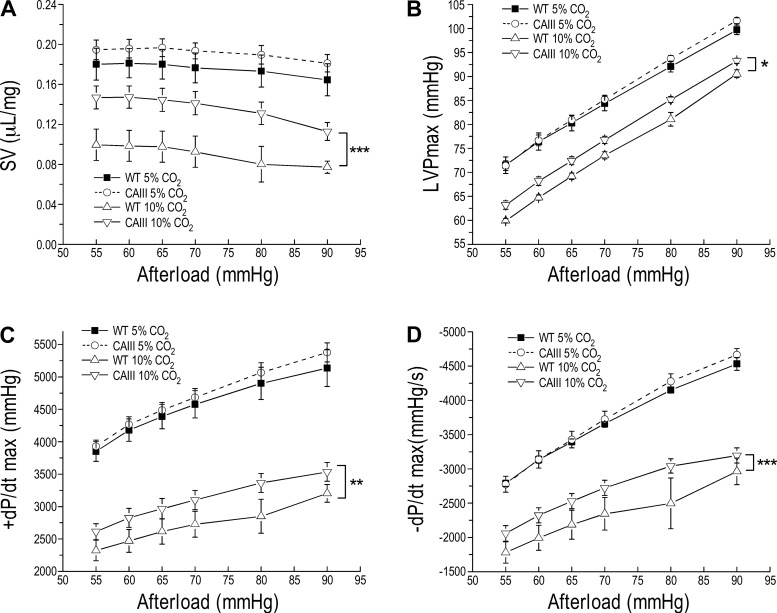
Fig. 4.
The higher resistance of carbonic anhydrase III (CAIII) transgenic mouse hearts to acidosis is sustained at high afterload. Ex vivo working-heart studies at heart rate of 480 beats/min, 10-mmHg preload, and increased afterload from 55 to 90 mmHg perfused at 90% O2-10% CO2, pH 7.06, vs. 95% O2-5% CO2, pH 7.36, demonstrated that the stroke volume (SV, A), left ventricular peak pressure (LVPmax, B), and maximum contractile and relaxation velocities (+dP/dt max and −dP/dt max, C and D, respectively) of CAIII transgenic mouse hearts responded to high afterload similarly to those of wild-type (WT) hearts at physiological pH. However, CAIII hearts showed higher resistance to acidosis than that of WT hearts by sustaining better function at high afterloads. Values are presented as means ± SE; n = 4 hearts in WT group, and n = 3 hearts in transgenic group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s adjustment for mean comparisons.