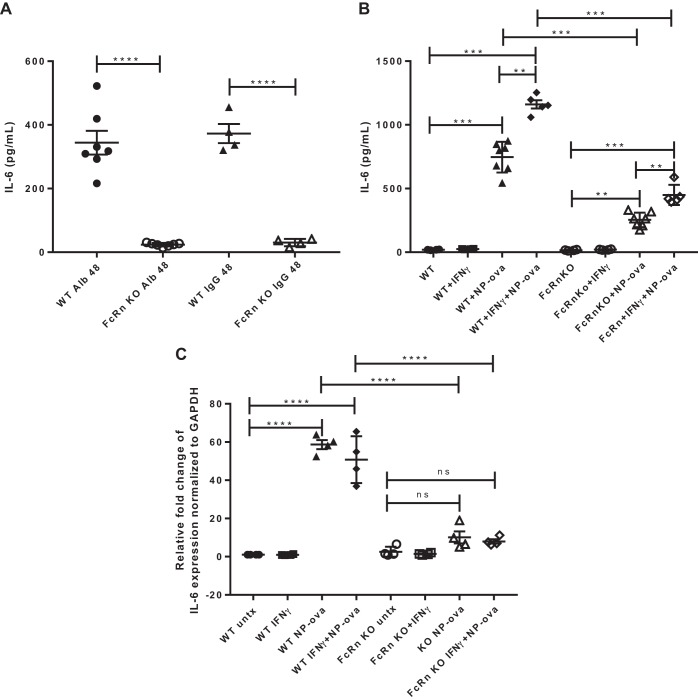
Fig. 1.
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) knockout (KO) podocytes produce significantly less IL-6 than wild type (WT) in response to albumin, IgG, or proinflammatory stimuli. A: IL-6 concentration in the supernatant harvested from WT or FcRn KO podocytes treated with albumin (Alb) or IgG for 48 h (n ≥ 4 experiments). B: IL-6 concentration in supernatant of WT and FcRn KO podocytes untreated (WT or KO) or treated with IFNɣ, 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylacetyl hapten-ovalbumin (NP-ova), or NP-ova plus IFNɣ for 48 h (n = ≥ 4 experiments). C: the relative fold change of IL-6 mRNA expression normalized to the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA level for untreated WT or KO podocytes (untx) or treated with IFNɣ or IFNɣ + NP-ova for 48 h (n = 4 experiments). Data are presented as means ± SE; ns, not statistically significant. In A–C, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.