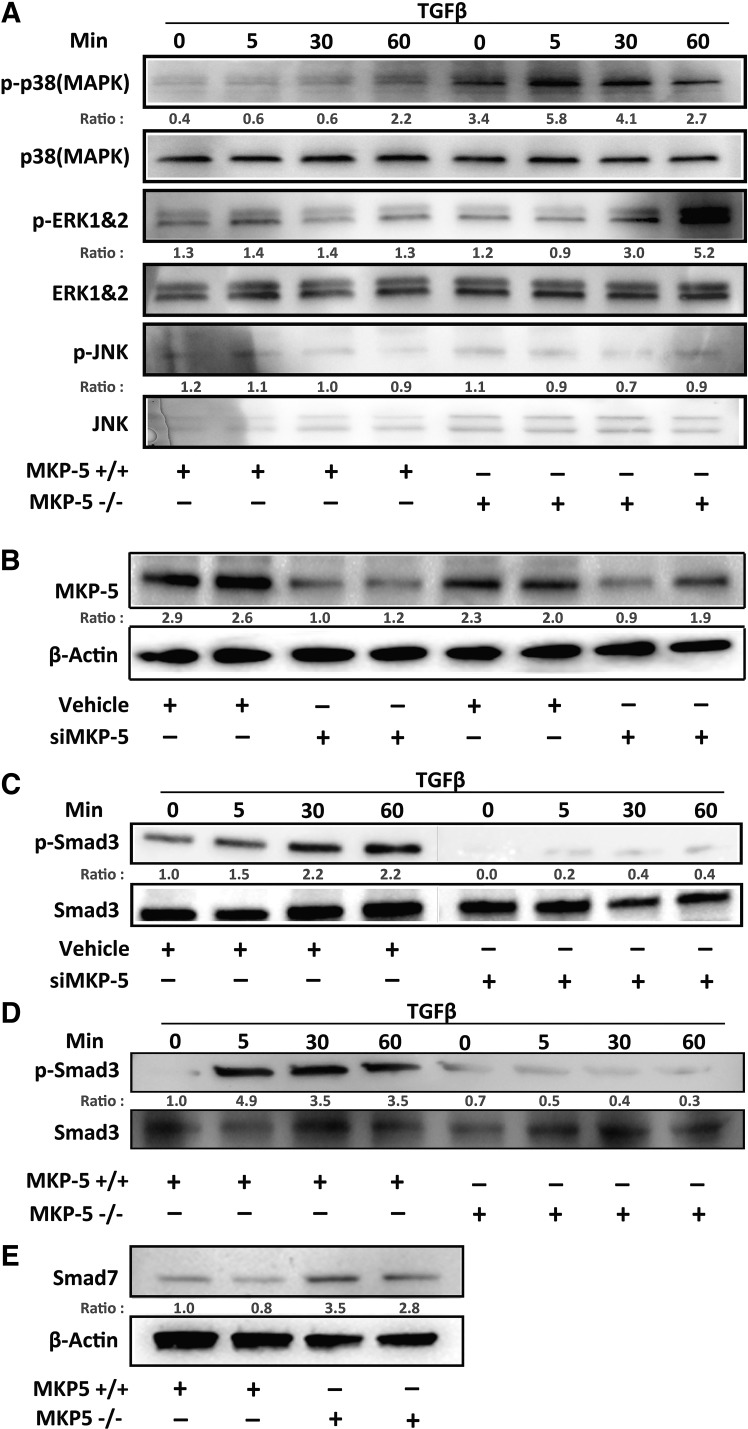
Fig. 3.
MAPK phosphatase 5 (MKP-5) inhibition negatively regulates transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1)-induced Smad3 fibrotic pathway. Primary mouse lung fibroblasts were isolated from C57BL/6, 9- to 12-week-old female mice in MKP-5 knockout (MKP-5−/−) or wild-type mice (MKP-5+/+), which were then stimulated with TGF-β1 (10 ng/mL) for 5, 30, and 60 min and then harvested for protein extraction and immunoblot analysis. Normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLFs) were transfected at 70% confluency with dual-specificity protein tyrosine phosphatase 10 (DUSP10)/MKP-5 siRNA (10 nM) for 24 h or a control nontargeting siRNA (10 nM). Cells were stimulated with TGF-β1 (10 ng/mL) for 5, 30, and 60 min. A: immunoblot analyses for phosphorylated (p-)MAPKs (p-JNK, p-ERK1/2, and p-p38 MAPK), along with their respective MAPK totals at the indicated time points of primary mouse lung fibroblast preparation from MKP-5+/+ and MKP-5−/− mice. B: immunoblot analyses for MKP-5 expression following transfection with DUSP10/MKP-5 siRNA (siMKP-5; 10 nM) or a nontargeting siRNA for 24 h (10 nM). Each lane represents an individual NHLF preparation. C: the same cell lysates were immunoblotted and analyzed for p-Smad3 and total Smad3 following TGF-β1 stimulation. D: immunoblot analysis for p-Smad3 and total Smad3 following TGF-β1 stimulation in primary lung fibroblasts from MKP-5+/+ and MKP-5−/− mice. E: immunoblot analysis for Smad7 in primary lung fibroblasts from MKP-5+/+ and MKP-5−/− fibroblasts. Ratio indicates protein densitometry ratio of the target/control protein.