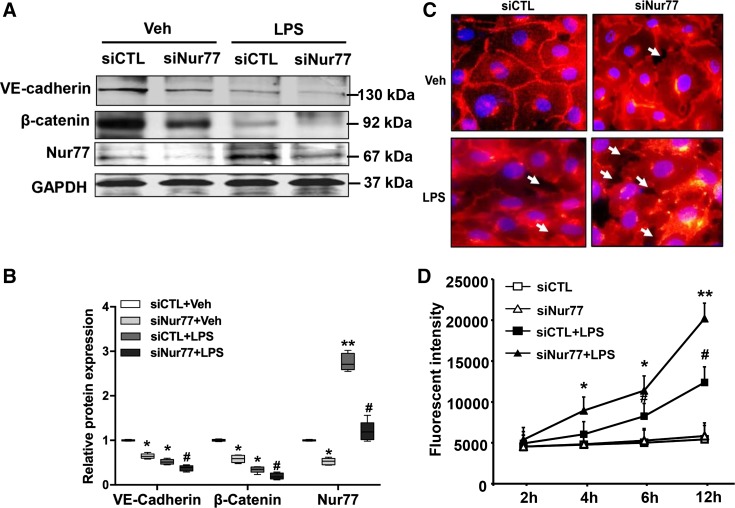
Fig. 5.
Nur77 knockdown promotes LPS-induced barrier dysfunction in lung microvascular endothelial cells. A: expression of vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin), β-catenin, and Nur77 in LPS-injured mouse lung microvessel endothelial cells (MLMECs) transfected with siCTL or siNur77. B: densitometry analysis of VE-cadherin, β-catenin, and Nur77 expression (n = 4). Veh, vehicle. *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01 vs. siCTL without LPS. #P < 0.05 vs. siCTL with LPS treatment. C: representative images of VE-cadherin in control and LPS-injured MLMECs after transfection with either siCTL or siNur77. Red color represents VE-cadherin; blue color corresponds to DAPI nuclear stain. D: levels of FITC-labeled dextran in the lower well of control and LPS-injured endothelial cell monolayers that have been transfected with either siCTL or siNur77 (100 ng/mL). FITC-dextran was measured using a fluorescence plate reader (BioTek) at 480/520 nm at the indicated time points. P < 0.05 vs. siCTL without LPS treatment (*) and siCTL with LPS treatment (#). **P < 0.01 vs. siCTL without LPS treatment.