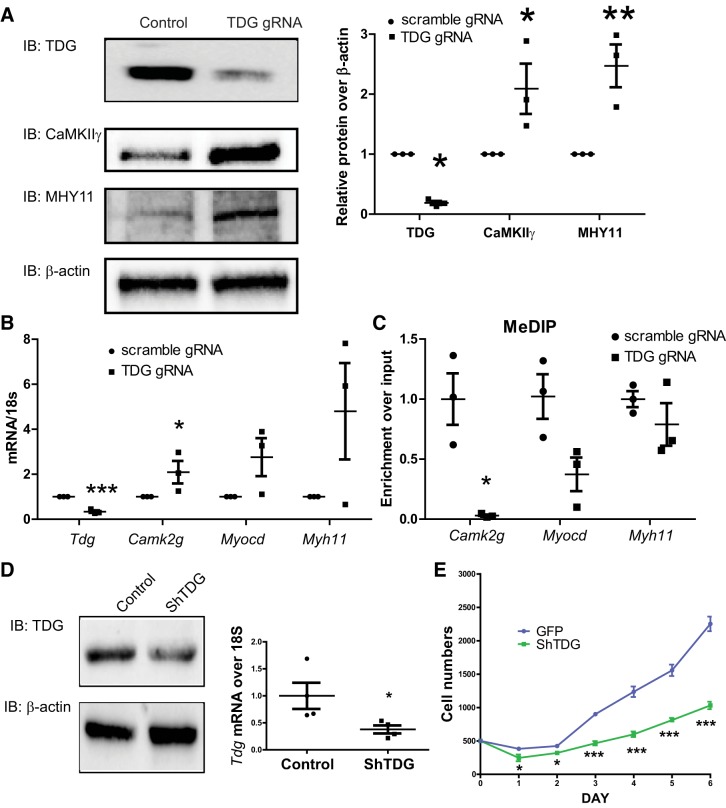
Fig. 6.
Thymine DNA glycosylase (TDG) suppression results in Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIγ (CaMKIIγ) promoter hypomethylation and increased CaMKIIγ expression in vascular smooth muscle synthetic phenotype (VSMSyn). Crispr/Cas9 all-in-one constructs expressing Cas9, scrambled guide RNA (gRNA), or TDG gRNA targeting Tdg exon3 were introduced into VSMSyn cells using lentivirus (A–C). Three days after infection, cells were collected for analysis of protein, mRNA, and genomic DNA. A: protein levels of TDG, CaMKIIγ, myosin heavy chain (MYH) 11, and β-actin were analyzed using SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with specific antibodies. B: quantitative PCR (qPCR) was used to determine Tdg, Camk2g, Myocd, and Myh11 mRNA expression. C: total genomic DNA was extracted from cultured cells infected with lentivirus-expressing scrambled gRNA and TDG gRNA. Methylated genomic DNA was purified by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP), and the enrichment of Camk2g, Myocd, and Myh11 promoters was analyzed by qPCR and specific primers. D: control lentivirus-expressing green fluorescent protein and scrambled RNA (control or GFP) or shRNA targeting TDG shTDG was used to infect VSMSyn cells for 3 days. The knockdown efficiency was examined by immunoblotting and qPCR. E: infected cells were resuspended and replated with identical cell numbers 3 days after lentivirus infection. The starting cell number was 500 for each sample, and cell numbers were counted every 24 h for a total of 6 days. All quantification was normalized over β-actin. Values shown are means ± SE. n = 3–4 analyzed by unpaired t test and 2-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.