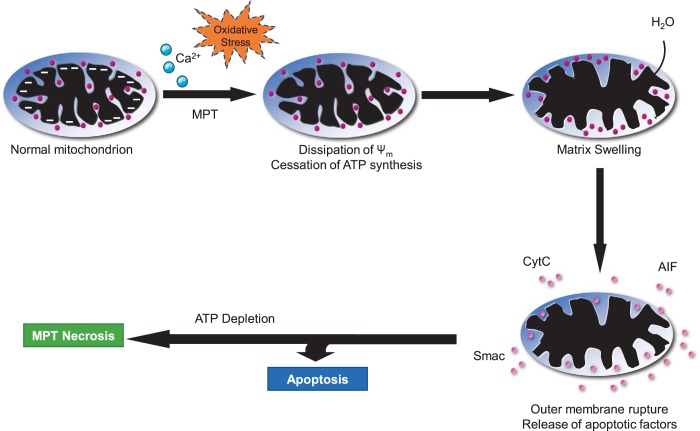
Fig. 3.
Mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT)-mediated necrosis. Because of calcium overload and/or extremely high oxidative stress, the mitochondrial membrane becomes permeable and results in dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential, leading to cessation of ATP synthesis. Increased permeability also causes influx of cytoplasmic water molecules, which causes matrix swelling that ultimately results in mitochondrial membrane rupture and release of apoptotic factors. In the presence of ATP, it leads to apoptosis. However, depletion of ATP causes MPT necrosis.