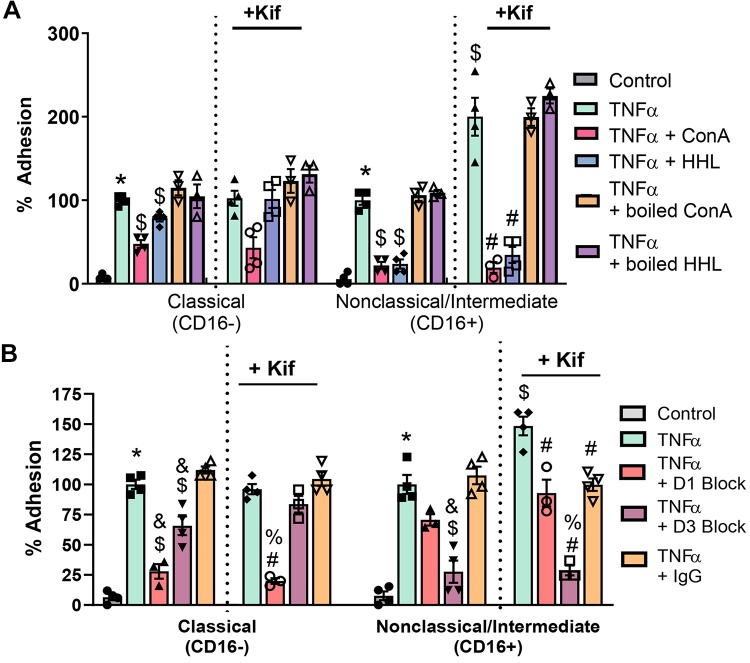
Fig. 5.
CD16+ monocyte adhesion is dependent on endothelial high-mannose (HM) epitopes and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). A: human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 4 h before monocyte adhesion assay. Some cells were pretreated with Kifunensine (Kif) to form HM epitopes on the cell surface, and then monocyte adhesion under flow was measured. Before adhesion assay, some cells were treated with the lectins Hippeastrum hybrid amaryllis (HHL) or concanavalin A (ConA) to block HM/hybrid N-glycans on the cell surface, or with denatured lectins to assess nonspecific binding effects. Each symbol represents the average of an independent experiment. Data are means ± SE, n = 3 or 4. P ≤ 0.05 compared with control (*), TNF-α alone ($), and TNF-α + Kif (#) by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s posttest within monocyte groups. B: HUVECs were treated as described, and some cells were treated with anti-ICAM-1 blocking antibodies that recognize domains 1 (D1) or 3 (D3) of ICAM-1 before monocyte adhesion assay. Each symbol represents the average of an independent experiment. Data are means ± SE, n = 3 or 4. P ≤ 0.05 compared with control (*), TNF-α ($), TNF-α + IgG control (&), TNF-α + Kif (#), and TNF-α + Kif + IgG control (%) by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s posttest within monocyte and cell treatment groups.