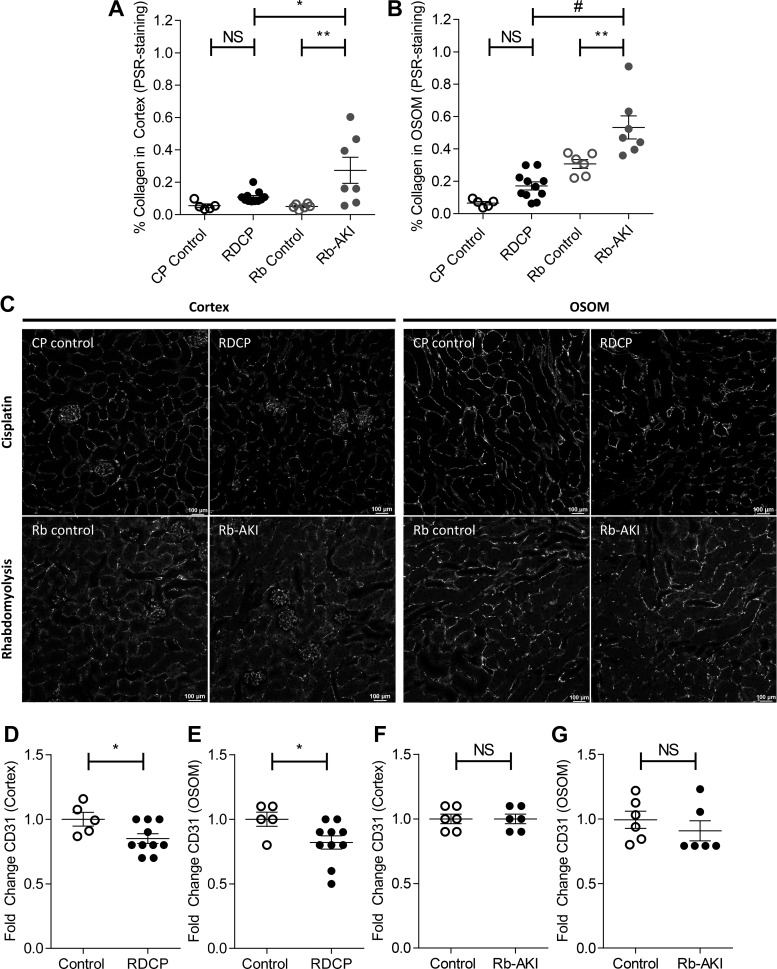
Fig. 6.
Renal fibrosis and capillary rarefaction in the repeated-dose cisplatin (RDCP) and rhabdomyolysis (Rb)-induced acute kidney injury (Rb-AKI) models. Quantification of fibrosis [picrosirius red (PSR) staining] was repeated to compare both models side by side. A and B: renal fibrosis (PSR staining) in the cortex (A) and outer stripe of the outer medulla (OSOM; B) at day 28 in RDCP and CP control mice and at day 36 in Rb-AKI and Rb control mice. C–G: capillary rarefaction was quantified as the fold change in CD31 staining in the cortex and OSOM at day 28 in CP-AKI and CP control mice (D and E) and at day 36 in Rb-AKI and Rb control mice (F and G). Data points represent individual animals, with means ± SE of the groups indicated. One-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance, and a post hoc Dunnett’s multiple-comparisons test was used to determine pairwise significance to compare RDCP vs. CP control, Rb-AKI vs. Rb control, and RDCP vs. Rb-AKI mice. P values were adjusted for multiple comparisons using Sidak’s multiple-comparison test. A two-sided t-test was used to compare RDCP and Rb-AKI groups with their respective control groups in D–G. NS, not significant (P > 0.05). *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; #P ≤ 0.0001.